If you’ve ever been prescribed anti-anxiety medication, you know the relief it can bring. These medications are often used to help manage anxiety disorders and provide much-needed calm in our hectic lives. But what happens when you decide to stop taking them abruptly? Well, my friend, that’s when the risks come into play. In this article, we will explore the potential dangers of stopping anti-anxiety medication abruptly and why it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider before making any changes to your medication regimen.
When it comes to managing anxiety, consistency is key. Anti-anxiety medications, such as benzodiazepines or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), work by regulating the chemicals in our brain responsible for anxiety. However, abruptly stopping these medications can disrupt the delicate balance that has been established, leading to a range of potential risks. From withdrawal symptoms to a resurgence of anxiety, the consequences can be significant.
So, why is it so important to consult with your healthcare provider before stopping your anti-anxiety medication? Well, they are the experts for a reason! They can guide you through the process, helping you to gradually taper off the medication and minimize the risks involved. Remember, your mental health is important, and making informed decisions about your treatment is crucial. So, let’s delve deeper into the potential risks of stopping anti-anxiety medication abruptly and why you should always seek professional guidance when considering any changes to your medication.
Stopping anti-anxiety medication abruptly can pose several risks. Withdrawal symptoms such as increased anxiety, irritability, insomnia, and even seizures may occur. Additionally, abruptly discontinuing medication can lead to a sudden recurrence of anxiety symptoms, making it difficult to manage daily life. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before making any changes to your medication regimen to ensure a safe and gradual tapering process.
Understanding the Risks of Stopping Anti-Anxiety Medication Abruptly
Taking medication for anxiety can be a vital part of managing the condition and improving quality of life. However, there may be instances where individuals consider stopping their anti-anxiety medication without consulting their healthcare provider. It is important to understand the potential risks associated with abruptly discontinuing these medications.
The Importance of Gradual Withdrawal
When it comes to anti-anxiety medication, abruptly stopping can have various negative effects on both physical and mental well-being. These medications are designed to regulate brain chemistry and help manage symptoms of anxiety. Abruptly discontinuing them can disrupt this delicate balance and lead to adverse reactions.
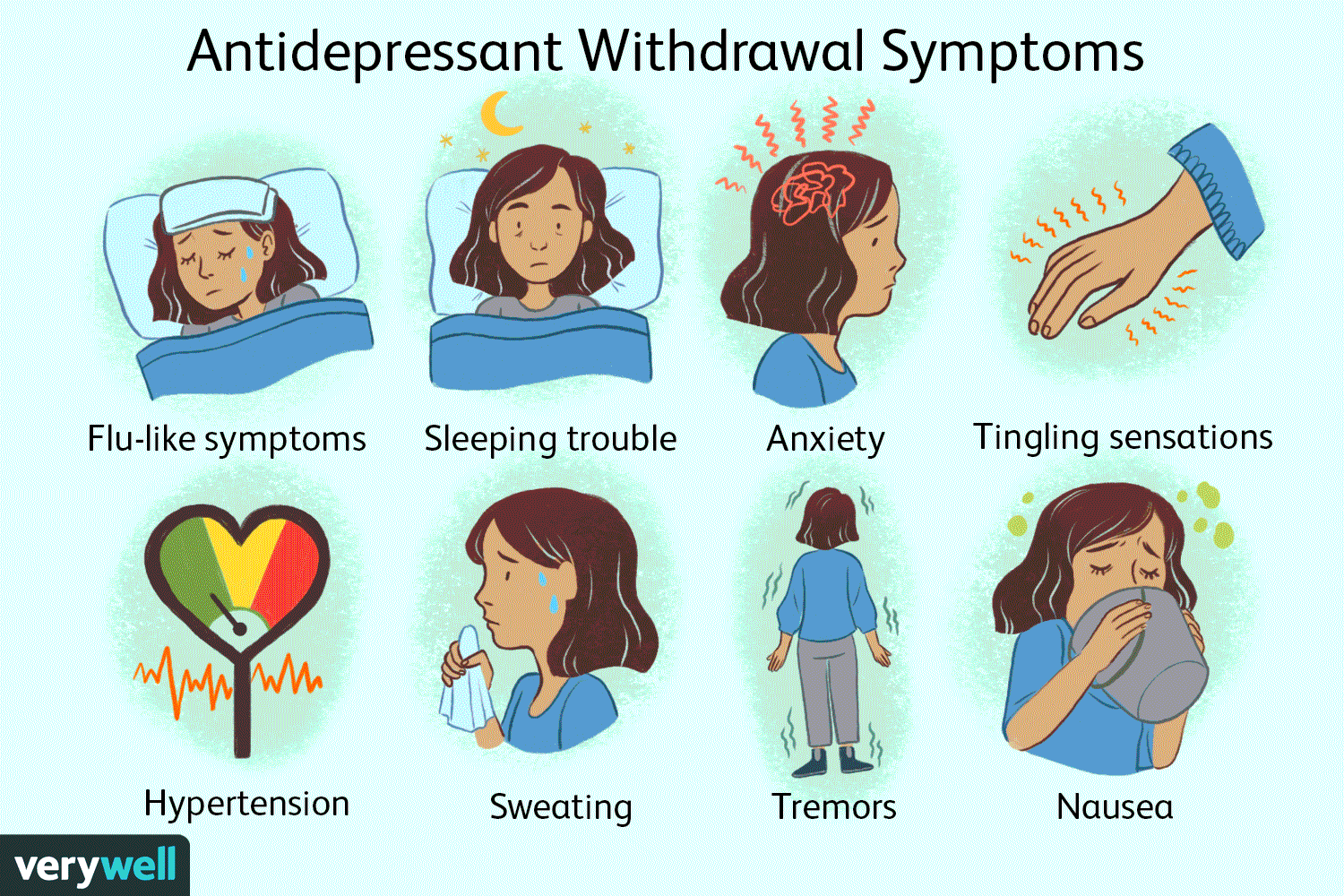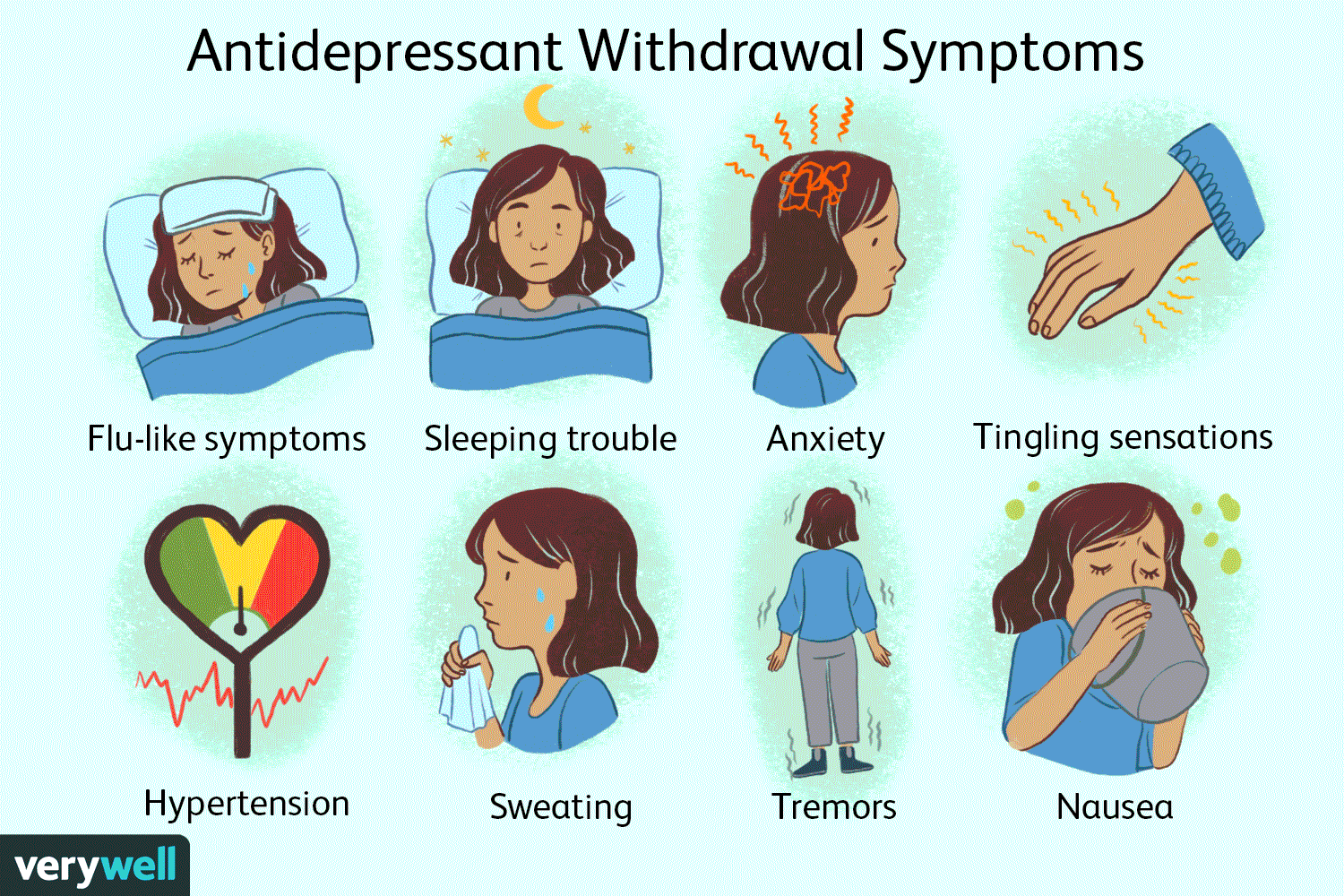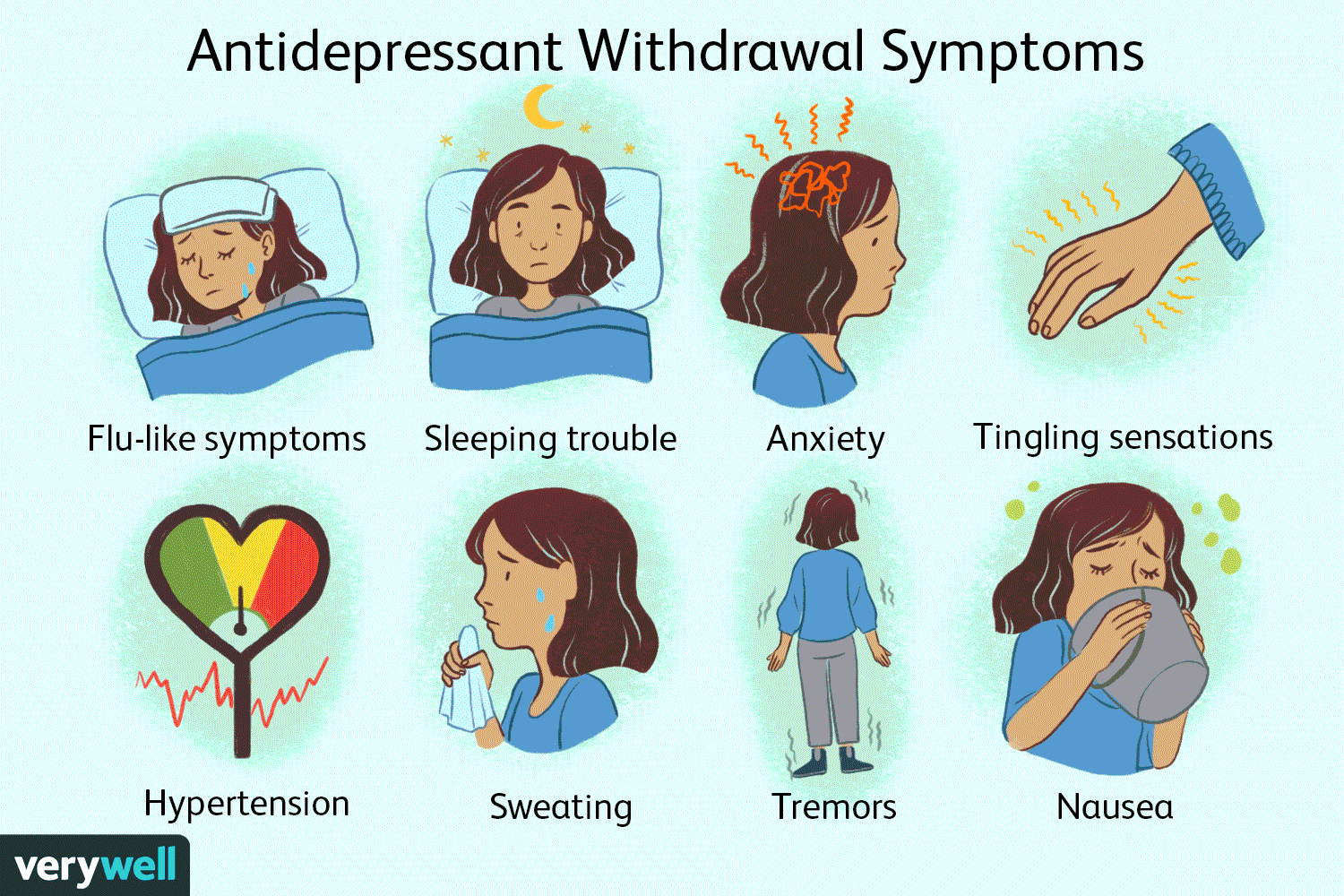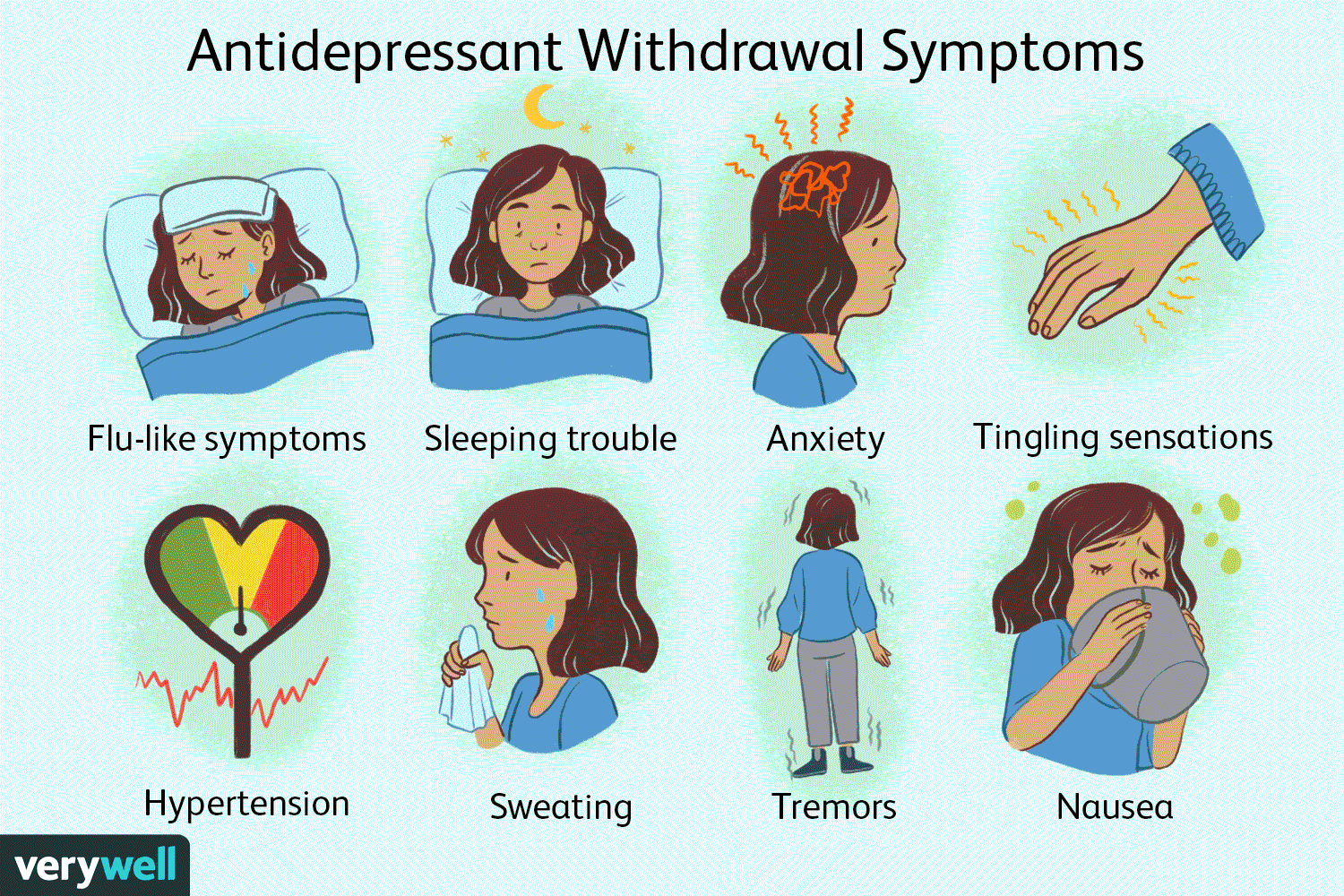
One of the primary reasons why gradual withdrawal is crucial is to avoid experiencing withdrawal symptoms. These symptoms can include increased anxiety, irritability, sleep disturbances, dizziness, and even flu-like symptoms. Gradually tapering off the medication allows the body to adjust slowly, minimizing the intensity of withdrawal symptoms.
Increased Anxiety and Relapse
One of the most significant risks of abruptly stopping anti-anxiety medication is the potential for increased anxiety and a higher risk of relapse. These medications help manage anxiety symptoms by regulating brain chemicals, such as serotonin and dopamine. Abruptly discontinuing them can lead to a sudden imbalance in these neurotransmitters, causing a surge in anxiety symptoms.
Additionally, abruptly stopping medication can make it more challenging for individuals to cope with anxiety triggers and manage their symptoms effectively. This can increase the risk of experiencing panic attacks or other anxiety-related episodes. It is essential to work closely with a healthcare professional to develop a plan for gradual withdrawal to minimize the risk of relapse.
Rebound Effect and Withdrawal Symptoms
Another potential risk of stopping anti-anxiety medication abruptly is the rebound effect. This refers to a sudden resurgence of anxiety symptoms that may be more intense than before starting the medication. The rebound effect can occur due to the sudden removal of the medication’s calming effects on the brain.
In addition to the rebound effect, individuals may also experience withdrawal symptoms when they abruptly stop taking their medication. These symptoms can vary depending on the specific medication but may include increased anxiety, restlessness, insomnia, nausea, and headaches. Gradual withdrawal allows the body to adjust slowly, minimizing the severity of these withdrawal symptoms.
The Importance of Healthcare Professional Guidance
When considering discontinuing anti-anxiety medication, it is crucial to seek guidance from a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized advice based on the individual’s specific circumstances and ensure a safe and effective withdrawal process.
Developing a Withdrawal Plan
A healthcare professional will assess the individual’s current medication regimen, overall health, and mental well-being to develop a tailored withdrawal plan. This plan typically involves gradually reducing the dosage of the medication over a specific period. The healthcare professional will closely monitor the individual’s progress and adjust the plan as necessary to ensure a smooth transition.
Alternative Strategies and Support
In addition to medication withdrawal, healthcare professionals can also recommend alternative strategies to manage anxiety symptoms. These may include therapy, lifestyle modifications, and stress reduction techniques. It is essential to have a comprehensive plan in place to address anxiety symptoms effectively while gradually tapering off the medication.
The Role of Open Communication
Open communication between the individual and their healthcare professional is vital throughout the medication withdrawal process. This includes discussing any concerns, side effects, or changes in symptoms that may arise. Regular check-ins with the healthcare professional provide an opportunity to address any challenges and adjust the withdrawal plan accordingly.
Seeking Support from Loved Ones
During the medication withdrawal process, it can be beneficial to seek support from loved ones. They can provide emotional support and understanding, especially during times when anxiety symptoms may be more challenging to manage. Having a strong support system can make the withdrawal process more manageable.
Patience and Self-Care
Lastly, it is crucial to practice patience and prioritize self-care during the medication withdrawal process. It may take time for the body and mind to adjust to the changes. Engaging in activities that promote relaxation, such as exercise, meditation, and hobbies, can help alleviate anxiety symptoms and promote overall well-being.
Understanding the Benefits of Gradual Medication Withdrawal
Gradually withdrawing from anti-anxiety medication offers several benefits for individuals who are considering stopping their medication. It allows the body and brain to adjust slowly, minimizing the risk of experiencing severe withdrawal symptoms and the rebound effect. It also provides an opportunity to explore alternative strategies for managing anxiety symptoms effectively.
Minimizing Withdrawal Symptoms
One of the primary benefits of gradual medication withdrawal is the ability to minimize the severity of withdrawal symptoms. Gradually reducing the dosage of the medication allows the body to adapt and minimize the impact of sudden changes. This can significantly reduce the discomfort associated with withdrawal and make the process more manageable.
Reducing the Risk of Relapse
By tapering off anti-anxiety medication gradually, individuals can reduce the risk of relapse. Abruptly stopping medication can disrupt the brain’s chemical balance, leading to a resurgence of anxiety symptoms. Gradual withdrawal allows the brain to adjust slowly, minimizing the likelihood of a relapse and providing a smoother transition.
Exploring Alternative Strategies
Gradual medication withdrawal provides an opportunity to explore alternative strategies for managing anxiety symptoms. This can involve therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. Lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress reduction techniques, can also be incorporated into the individual’s anxiety management plan.
The Importance of Professional Guidance
When considering gradual medication withdrawal, it is crucial to seek guidance from a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized advice and develop a tailored plan based on the individual’s specific needs and circumstances.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting the Plan
A healthcare professional will closely monitor the individual’s progress throughout the medication withdrawal process. Regular check-ins provide an opportunity to assess any changes in symptoms, address concerns, and make necessary adjustments to the withdrawal plan. This ensures that the individual’s needs are met and that the withdrawal process remains safe and effective.
Addressing Underlying Factors
During the medication withdrawal process, healthcare professionals can also address any underlying factors contributing to anxiety. This may involve exploring potential triggers, addressing unresolved trauma, or identifying and managing co-occurring mental health conditions. By addressing these factors, individuals can have a more comprehensive approach to managing their anxiety symptoms.
Conclusion
Gradually withdrawing from anti-anxiety medication is essential to minimize the risks associated with abrupt discontinuation. It allows the body and brain to adjust slowly, reducing the likelihood of experiencing withdrawal symptoms and the rebound effect. Working closely with a healthcare professional throughout the withdrawal process ensures a safe and effective transition. Additionally, exploring alternative strategies and addressing underlying factors can support individuals in managing their anxiety symptoms effectively. Remember, always seek professional guidance when considering any changes to your medication regimen.
Key Takeaways: What are the risks of stopping anti-anxiety medication abruptly?
- Stopping anti-anxiety medication abruptly can lead to withdrawal symptoms.
- Withdrawal symptoms may include increased anxiety, irritability, and insomnia.
- Stopping medication abruptly can also cause a rebound effect, worsening anxiety symptoms.
- It is important to gradually taper off medication under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- Abruptly stopping medication can increase the risk of relapse and make it harder to manage anxiety in the long term.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How can abruptly stopping anti-anxiety medication be risky?
A: Abruptly stopping anti-anxiety medication can be risky due to several reasons. Firstly, these medications are often prescribed to manage anxiety disorders, which can cause severe withdrawal symptoms when stopped suddenly. These symptoms may include rebound anxiety, insomnia, irritability, and even panic attacks.
Secondly, abruptly stopping medication can disrupt the delicate balance of chemicals in the brain that these medications help regulate. This can lead to a sudden increase in anxiety symptoms, as well as other withdrawal effects such as dizziness, nausea, and headaches. It is important to gradually reduce the dosage of anti-anxiety medication under the guidance of a healthcare professional to minimize these risks.
Q: Can abruptly stopping anti-anxiety medication lead to a relapse of anxiety?
A: Yes, abruptly stopping anti-anxiety medication can increase the risk of a relapse of anxiety symptoms. These medications are often prescribed to help manage and control anxiety disorders, and abruptly stopping them can disrupt the progress made in managing anxiety.
When medication is suddenly stopped, the brain may experience a rebound effect, where anxiety symptoms become more intense than before. This can lead to a relapse of anxiety, potentially causing significant distress and impairment in daily functioning. Gradually tapering off the medication under medical supervision is important to minimize the risk of relapse.
Q: Are there any specific medications that pose higher risks when stopped abruptly?
A: While abruptly stopping any anti-anxiety medication can be risky, certain medications may pose higher risks than others. Benzodiazepines, such as Xanax and Valium, are known to have a higher potential for dependence and withdrawal symptoms when stopped suddenly.
These medications work by enhancing the effects of a neurotransmitter called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which helps calm the brain. Abruptly stopping benzodiazepines can lead to a sudden decrease in GABA activity, causing withdrawal symptoms that can be severe. It is important to work closely with a healthcare professional when discontinuing benzodiazepines or any other medication to minimize these risks.
Q: How long do withdrawal symptoms typically last after stopping anti-anxiety medication abruptly?
A: The duration of withdrawal symptoms after abruptly stopping anti-anxiety medication can vary depending on several factors, including the specific medication, dosage, and individual physiology. In general, withdrawal symptoms may begin within a few days to a week after discontinuation and can last for several weeks or even months.
However, it is important to note that everyone’s experience with withdrawal can be different. Some individuals may experience milder symptoms that subside relatively quickly, while others may experience more intense and prolonged symptoms. Working closely with a healthcare professional during the discontinuation process can help manage and minimize the duration and severity of withdrawal symptoms.
Q: What are some strategies to safely taper off anti-anxiety medication?
A: Tapering off anti-anxiety medication should always be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional to ensure safety and minimize risks. Some common strategies for a safe taper include gradually reducing the dosage over a period of time, sometimes weeks or months, depending on the medication.
Other strategies may include switching to a longer-acting medication before tapering off or using adjunctive therapies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy, to help manage anxiety symptoms during the tapering process. It is crucial to work closely with a healthcare professional to develop an individualized tapering plan that takes into account the specific medication, dosage, and individual needs.
Antidepressant Discontinuation Syndrome | Medications, Signs & Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
Final Thoughts:
When it comes to stopping anti-anxiety medication abruptly, the risks are not to be taken lightly. It’s crucial to approach this decision with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Abruptly discontinuing these medications can lead to a range of potential risks and adverse effects.
One significant risk of stopping anti-anxiety medication abruptly is the possibility of experiencing withdrawal symptoms. These symptoms can vary depending on the specific medication being used and the individual’s unique physiology. They may include increased anxiety, irritability, insomnia, dizziness, nausea, and even seizures in severe cases. It’s important to remember that the purpose of these medications is to regulate brain chemistry and provide relief from anxiety disorders. Abruptly ceasing their use disrupts this delicate balance, leading to withdrawal symptoms and potential rebound anxiety.
Another risk to consider is the potential for a relapse or worsening of anxiety symptoms. Anti-anxiety medications are often prescribed to manage and control anxiety disorders. Stopping them abruptly without a proper plan in place can leave individuals vulnerable to the reemergence of anxiety symptoms. This can significantly impact their overall well-being and quality of life. It’s crucial to work closely with a healthcare professional to develop a tapering schedule or alternative treatment plan to minimize the risk of relapse.
In conclusion, the decision to stop anti-anxiety medication should never be taken lightly. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide guidance and support throughout the process. Abruptly discontinuing these medications can lead to withdrawal symptoms, rebound anxiety, and potential relapse. By working closely with a healthcare professional, individuals can safely navigate this decision and explore alternative treatment options if necessary. Your mental health is important, and taking the necessary steps to prioritize it is key.



