Are you curious about the potential long-term effects of using anti-anxiety medication? Let’s dive into this topic and explore the possible impacts that these medications may have on individuals over an extended period of time. In today’s fast-paced world, where stress and anxiety are common, many people turn to medication to manage their symptoms and find relief. However, it’s important to understand the potential consequences that may arise from long-term use.
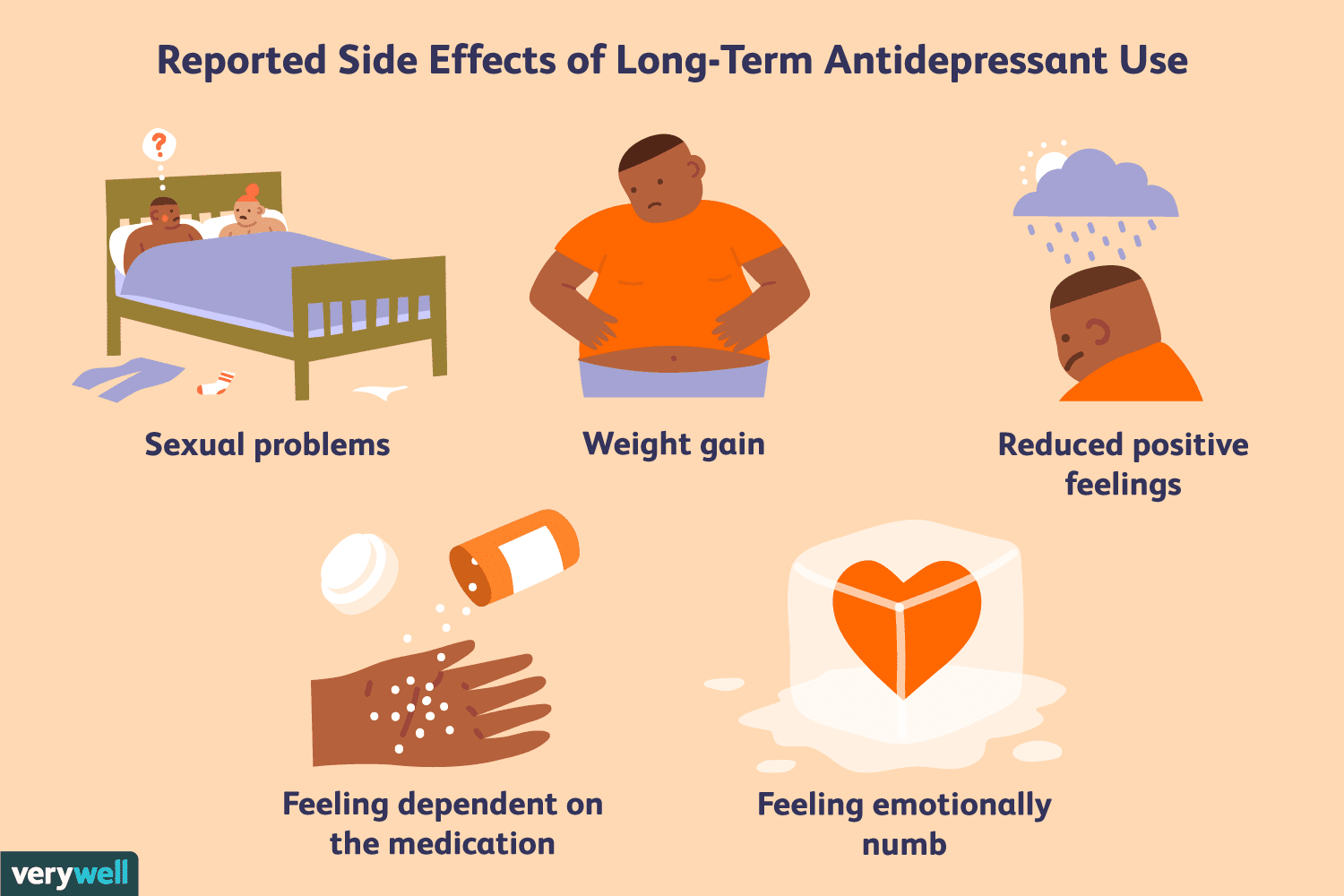
When it comes to anti-anxiety medication, there are various types available, such as benzodiazepines and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). While these medications can be beneficial in the short-term, providing relief from anxiety and panic attacks, there are concerns about their long-term effects. Some studies suggest that prolonged use of benzodiazepines can lead to issues like cognitive impairment, memory problems, and even an increased risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. On the other hand, SSRIs, which are commonly prescribed for anxiety disorders, may have side effects such as weight gain, sexual dysfunction, and emotional blunting.
As more research is conducted on the long-term effects of anti-anxiety medication, it is crucial for individuals to weigh the potential benefits against the possible risks. It’s always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action for managing anxiety and to explore alternative therapies that may be effective in reducing symptoms. Remember, your well-being is important, and understanding the potential long-term effects of any medication is a crucial step in making informed decisions about your health.
What are the Potential Long-Term Effects of Using Anti-Anxiety Medication?
Anti-anxiety medications are commonly prescribed to help individuals manage their anxiety symptoms. While these medications can be effective in the short-term, it is important to consider the potential long-term effects they may have on the body and mind. Understanding these potential effects can help individuals make informed decisions about their mental health treatment. Here, we will explore some of the long-term effects of using anti-anxiety medication.
1. Dependency and Addiction
One of the potential long-term effects of using anti-anxiety medication is the development of dependency and addiction. Anti-anxiety medications, such as benzodiazepines, work by modulating the brain’s neurotransmitters to reduce anxiety. However, continued use of these medications can lead to tolerance, meaning higher doses are needed to achieve the same effect. This can increase the risk of dependency and addiction.
Dependency
Dependency occurs when the body becomes reliant on the medication to function properly. Suddenly stopping the medication or reducing the dosage can lead to withdrawal symptoms, such as rebound anxiety, sleep disturbances, and irritability. Individuals may feel trapped in a cycle of needing the medication to manage their anxiety, which can be challenging to break free from.
Addiction
Addiction, on the other hand, is a psychological dependence on the medication. It involves compulsive drug-seeking behavior, despite negative consequences. Individuals may find themselves craving the medication and using it in ways that are not prescribed, such as taking higher doses or seeking additional sources. Addiction to anti-anxiety medication can have serious implications for one’s health and overall well-being.
2. Cognitive Impairment
Another potential long-term effect of using anti-anxiety medication is cognitive impairment. Some individuals may experience difficulties with memory, attention, and concentration while taking these medications. This can impact daily functioning and quality of life. It is important to note that not everyone will experience cognitive impairment, and the severity of these effects can vary from person to person.
Memory Issues
Memory issues are a common cognitive side effect of anti-anxiety medications. Individuals may experience difficulties with short-term memory, including forgetfulness and difficulty retaining new information. This can make it challenging to perform tasks that require concentration and recall, such as studying or completing work assignments.
Attention and Concentration Problems
Anti-anxiety medications can also affect attention and concentration. Some individuals may find it harder to focus on tasks or sustain attention for prolonged periods. This can impact productivity and performance in various areas of life, including work, school, and personal relationships.
3. Physical Health Risks
In addition to the psychological and cognitive effects, long-term use of anti-anxiety medication can also pose certain physical health risks. It is important for individuals to be aware of these potential risks and discuss them with their healthcare provider.
Respiratory Issues
Certain anti-anxiety medications, such as benzodiazepines, can suppress the respiratory system, especially when taken in high doses or combined with other substances. This can lead to breathing difficulties, particularly in individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions. It is crucial to use these medications as prescribed and under the guidance of a healthcare professional to minimize the risk of respiratory issues.
Sleep Disturbances
Some individuals may experience sleep disturbances as a result of taking anti-anxiety medication. These disturbances can range from difficulty falling asleep to disruptions in the sleep cycle. Poor sleep quality can impact overall well-being and contribute to other health issues, such as fatigue and impaired cognitive function.
In conclusion, while anti-anxiety medications can provide relief for individuals struggling with anxiety, it is essential to consider the potential long-term effects they may have. Dependency and addiction, cognitive impairment, and physical health risks are some of the factors to be mindful of. It is crucial to work closely with a healthcare professional to carefully monitor the use of these medications and explore alternative treatment options when appropriate.
Key Takeaways: What are the potential long-term effects of using anti-anxiety medication?
- Long-term use of anti-anxiety medication may lead to dependency and addiction.
- Some individuals may experience cognitive impairment or memory problems as a result of prolonged use.
- Weight gain or loss can occur as a side effect of using these medications over an extended period.
- Long-term use may increase the risk of experiencing withdrawal symptoms when discontinuing the medication.
- Regular monitoring and consultation with a healthcare professional are essential to manage potential long-term effects.
Frequently Asked Questions
When it comes to using anti-anxiety medication, many people wonder about the potential long-term effects. It’s important to note that each person’s experience may vary, and it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice. However, here are some commonly asked questions and answers about the potential long-term effects of using anti-anxiety medication.
Question 1: Can anti-anxiety medication cause dependence?
While anti-anxiety medication can be effective in managing symptoms, some medications, such as benzodiazepines, can lead to dependence if used for extended periods. It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions carefully and not exceed the prescribed dosage. If you have concerns about dependence, speak with your doctor, who may recommend alternative treatment options or a gradual tapering off of the medication.
Additionally, it’s worth noting that not all anti-anxiety medications have the same potential for dependence. Some newer medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), are generally considered to have a lower risk of dependence compared to benzodiazepines.
Question 2: Are there any cognitive side effects associated with long-term use of anti-anxiety medication?
In some cases, long-term use of anti-anxiety medication may be associated with cognitive side effects. These can include difficulties with memory, attention, or concentration. However, it’s important to remember that individual responses to medication can vary, and not everyone will experience these side effects. It’s always a good idea to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider, who can help monitor your cognitive function and make adjustments to your treatment plan if necessary.
Furthermore, newer generations of anti-anxiety medications, such as SSRIs or SNRIs, are generally associated with fewer cognitive side effects compared to older medications like benzodiazepines. Your doctor can help determine the most suitable medication for your specific needs.
Question 3: Can long-term use of anti-anxiety medication lead to weight changes?
Weight changes are a potential side effect of some anti-anxiety medications. While some individuals may experience weight gain, others may experience weight loss. The specific medication you are taking, as well as individual factors, can influence these changes. It’s important to maintain open communication with your healthcare provider about any noticeable changes in your weight, as they can provide guidance and support.
If you are concerned about weight changes, your doctor may consider alternative treatment options or recommend lifestyle modifications, such as regular exercise and a balanced diet, to help manage any potential weight-related effects.
Question 4: What are the potential effects on sexual function with long-term use of anti-anxiety medication?
Some individuals may experience changes in sexual function as a result of long-term use of anti-anxiety medication. These changes can include decreased libido, difficulty achieving orgasm, or erectile dysfunction. It’s important to remember that not everyone will experience these effects, and individual responses to medication can vary.
If you notice any changes in your sexual function while taking anti-anxiety medication, it’s important to discuss them with your healthcare provider. They can provide guidance and explore potential solutions, such as adjusting your medication or considering additional treatment options.
Question 5: Are there any potential long-term effects on mood or emotional well-being?
While anti-anxiety medication is often prescribed to help manage mood and emotional well-being, there is a possibility of long-term effects on these aspects. Some individuals may experience changes in mood, such as increased irritability or emotional blunting. It’s important to remember that individual responses to medication can vary, and not everyone will experience these effects.
If you have concerns about the long-term effects of anti-anxiety medication on your mood or emotional well-being, it’s important to discuss them with your healthcare provider. They can evaluate your treatment plan and make adjustments as needed to help optimize your overall well-being.
Seth Doane on the growing addiction to anti-anxiety medication, debilitating withdrawal symptoms
Final Thoughts
After exploring the potential long-term effects of using anti-anxiety medication, it’s clear that while these medications can provide significant relief for individuals struggling with anxiety disorders, they also come with some potential risks and considerations. It’s important to approach the use of these medications with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
While anti-anxiety medications can help manage symptoms in the short term, prolonged use may lead to dependence and withdrawal symptoms when trying to discontinue them. This highlights the importance of carefully monitoring medication usage and working closely with a healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive treatment plan.
Additionally, some studies suggest that long-term use of certain anti-anxiety medications may be associated with cognitive impairment and an increased risk of developing other mental health conditions. This emphasizes the need for regular evaluations and open communication with your healthcare provider to ensure that the benefits of these medications continue to outweigh any potential risks.
In conclusion, anti-anxiety medications can be valuable tools in managing anxiety disorders, but they should be used judiciously and in conjunction with other therapeutic approaches. It’s essential to have ongoing discussions with your healthcare provider to assess the long-term effects, weigh the benefits against the risks, and make informed decisions about your treatment journey. Remember, you are not alone in this process, and together with your healthcare team, you can find the most effective and sustainable approach to managing anxiety and improving your overall well-being.