So, you’re curious about the role of serotonin in anxiety? Well, buckle up and get ready for a wild ride into the intricate workings of our brain chemistry! Anxiety is a common experience that many of us face at some point in our lives, and understanding the role of serotonin can shed some light on why it happens and how it affects us. So, let’s dive in and explore this fascinating topic together!
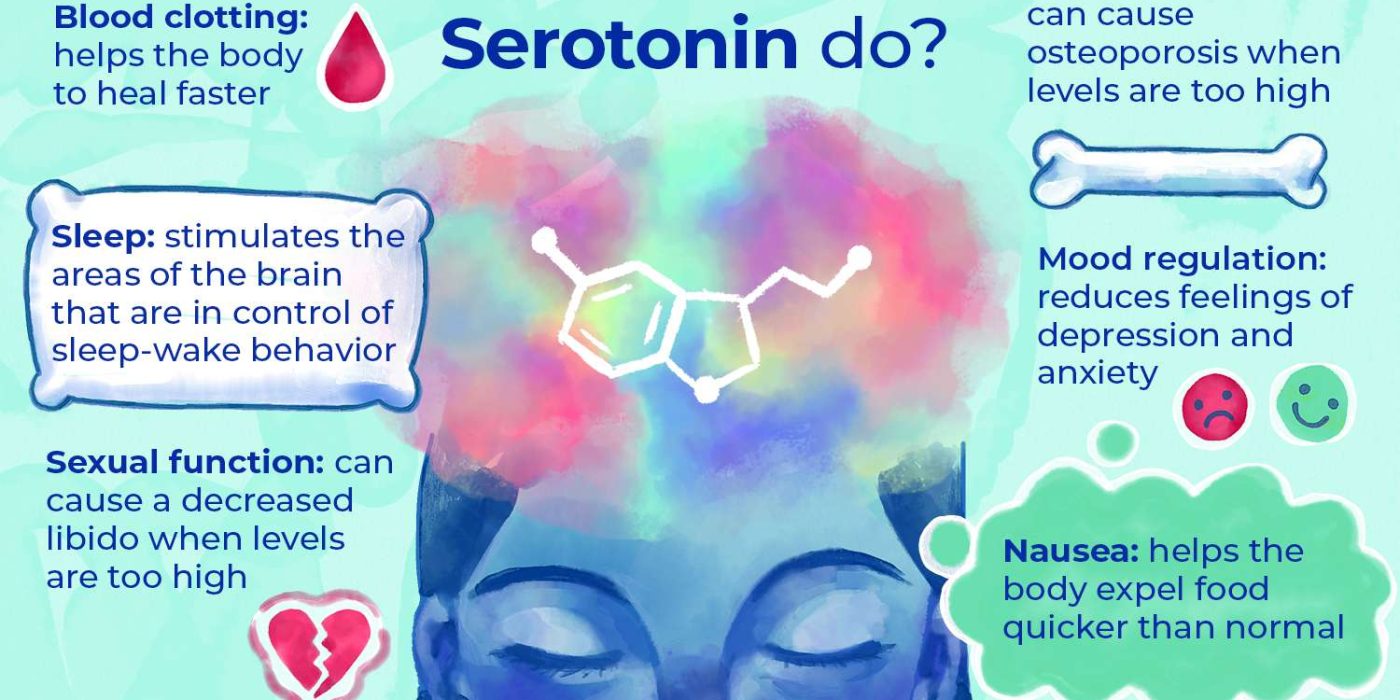
Now, when it comes to anxiety, serotonin plays a crucial role as one of the key neurotransmitters involved. Neurotransmitters are like messengers in our brain, relaying important signals between nerve cells. Serotonin, often referred to as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter, helps regulate mood, sleep, appetite, and yes, you guessed it, anxiety. It’s like the conductor of an orchestra, making sure all the instruments are playing in harmony.
But here’s where things get interesting. When there’s an imbalance or dysfunction in serotonin levels, it can lead to an increase in anxiety symptoms. Think of it like a car engine running on low fuel – it’s not going to function at its best. Similarly, when serotonin levels are low, it can throw off the delicate balance of our brain chemistry, leading to feelings of unease, worry, and restlessness. So, understanding the role of serotonin in anxiety is crucial for finding ways to restore that balance and bring back the calm.
Understanding the Role of Serotonin in Anxiety
Anxiety is a common mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by feelings of fear, worry, and apprehension. While the exact causes of anxiety are complex and multifaceted, researchers have identified a number of factors that contribute to its development. One such factor is the neurotransmitter serotonin.
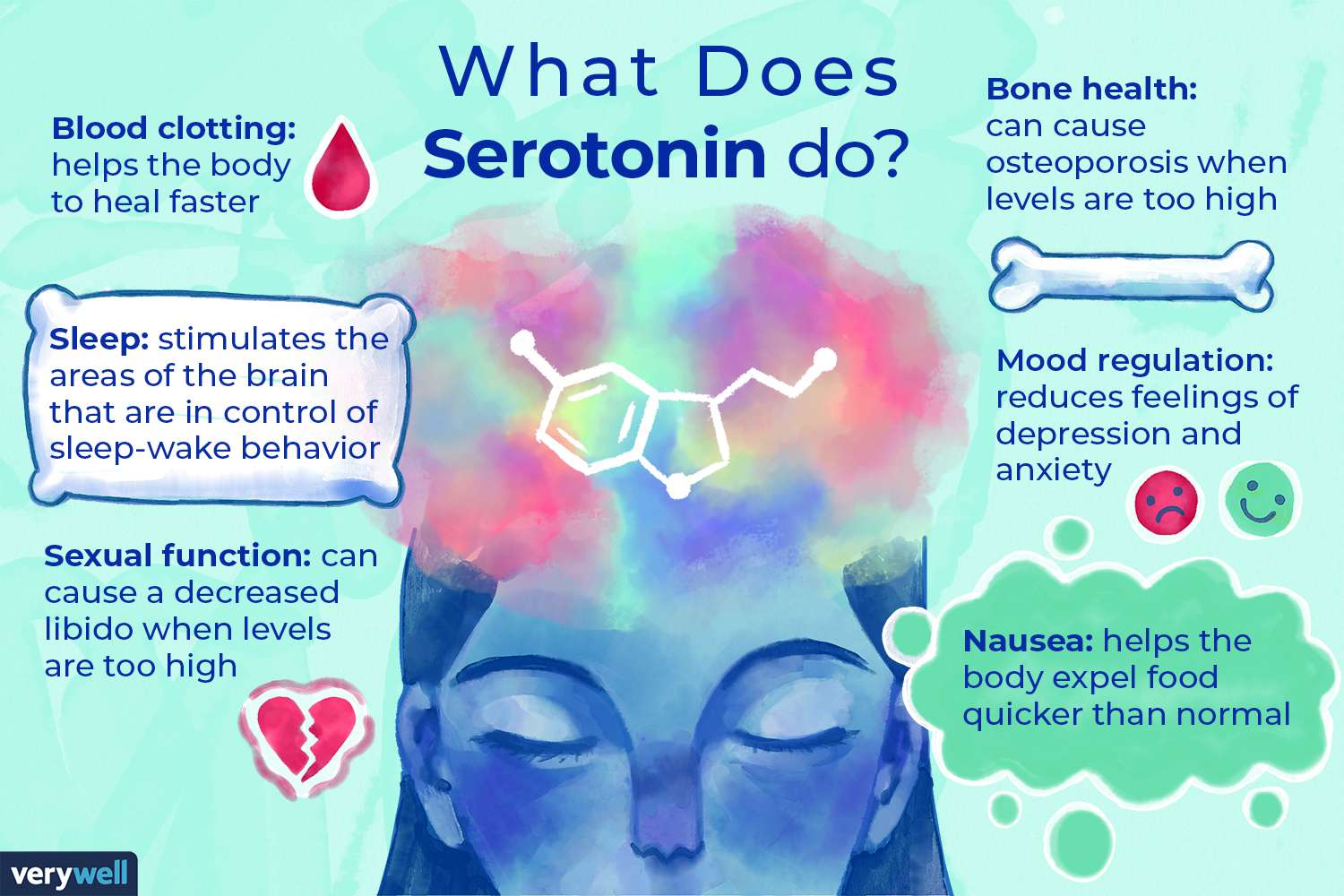
Serotonin is a chemical messenger that plays a crucial role in regulating mood, sleep, appetite, and other important functions in the body. It is often referred to as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter because it helps to promote feelings of well-being and happiness. However, when serotonin levels become imbalanced, it can contribute to the development of anxiety disorders.
The Role of Serotonin in Anxiety
1. Serotonin and the Brain:
Serotonin is primarily produced in the brain and is responsible for regulating mood and emotions. It helps to regulate the activity of other neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and norepinephrine, which are also involved in mood regulation. When serotonin levels are low, it can lead to an imbalance in these neurotransmitters, contributing to symptoms of anxiety.
2. Serotonin and the Amygdala:
The amygdala is a small almond-shaped structure in the brain that is responsible for processing emotions, including fear and anxiety. Serotonin helps to regulate the activity of the amygdala, preventing it from becoming overactive. When serotonin levels are low, it can lead to increased amygdala activity, resulting in heightened anxiety responses.
The Role of Serotonin in Anxiety Disorders
1. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD):
Individuals with GAD experience excessive and uncontrollable worry about a wide range of everyday concerns. Studies have shown that serotonin imbalances may contribute to the development and maintenance of GAD symptoms. Medications that increase serotonin levels, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), are commonly prescribed to help manage GAD.
2. Panic Disorder:
Panic disorder is characterized by recurrent panic attacks, which are sudden episodes of intense fear and physical symptoms such as heart palpitations and shortness of breath. Serotonin imbalances have been implicated in the development of panic disorder, and medications that enhance serotonin function can help reduce the frequency and severity of panic attacks.
3. Social Anxiety Disorder:
Individuals with social anxiety disorder experience intense fear and discomfort in social situations. Research suggests that serotonin imbalances may play a role in the development of social anxiety disorder. Medications that increase serotonin levels can help reduce social anxiety symptoms and improve overall functioning.
How to Increase Serotonin Levels Naturally
While medications can help manage anxiety symptoms by increasing serotonin levels, there are also natural ways to boost serotonin production in the body:
- Regular exercise: Physical activity has been shown to increase serotonin levels and improve mood.
- Healthy diet: Consuming foods rich in tryptophan, such as turkey, eggs, and nuts, can promote serotonin production.
- Sunlight exposure: Spending time outdoors and getting natural sunlight can help increase serotonin levels.
- Stress management: Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and meditation, can help reduce stress and promote serotonin production.
- Social support: Maintaining strong social connections and engaging in fulfilling relationships can contribute to increased serotonin levels.
Conclusion
Serotonin plays a crucial role in regulating mood and emotions, and imbalances in serotonin levels can contribute to the development of anxiety disorders. Understanding the role of serotonin in anxiety can help individuals and healthcare professionals better understand and manage these conditions. By increasing serotonin levels through medication or natural methods, individuals with anxiety can experience relief from their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
Key Takeaways: The Role of Serotonin in Anxiety
- Serotonin is a chemical in the brain that helps regulate mood and emotions.
- Low levels of serotonin have been linked to increased anxiety and feelings of unease.
- Boosting serotonin levels can help reduce anxiety symptoms and promote a sense of calm.
- Medications that increase serotonin activity, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), are often prescribed for anxiety disorders.
- Other techniques like exercise, relaxation practices, and therapy can also help increase serotonin levels and manage anxiety.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the effects of serotonin on anxiety?
Serotonin, a neurotransmitter commonly associated with mood regulation, also plays a crucial role in anxiety. When serotonin levels are low, it can lead to increased anxiety symptoms. This is because serotonin helps regulate emotions and promote feelings of calmness and well-being. When there is an imbalance or deficiency of serotonin, it can disrupt the brain’s ability to regulate anxiety effectively.
On the other hand, optimal levels of serotonin help to reduce anxiety by promoting a sense of relaxation and reducing the body’s stress response. Serotonin activates specific receptors in the brain that help modulate anxiety levels, making it an important player in anxiety management.
How does serotonin affect anxiety disorders?
Serotonin plays a crucial role in the development and management of anxiety disorders. In individuals with anxiety disorders, there may be an imbalance or dysfunction in the serotonin system. This can lead to decreased serotonin activity and an increased risk of experiencing anxiety symptoms.
By understanding the role of serotonin in anxiety disorders, researchers have developed medications known as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) that specifically target the serotonin system. SSRIs work by increasing the availability of serotonin in the brain, which can help alleviate anxiety symptoms and improve overall mood.
Can low serotonin levels cause anxiety?
Low serotonin levels have been linked to increased anxiety symptoms. Serotonin helps regulate mood and emotions, and when levels are low, it can lead to a dysregulation of anxiety. Low serotonin levels can make individuals more susceptible to experiencing anxiety and may contribute to the development of anxiety disorders.
It’s important to note that anxiety is a complex condition influenced by various factors, and serotonin is just one piece of the puzzle. While low serotonin levels can contribute to anxiety, it is not the sole cause. Other factors such as genetics, environment, and life experiences also play a significant role in the development and manifestation of anxiety.
How can serotonin be increased naturally to reduce anxiety?
While medications can help increase serotonin levels, there are also natural ways to boost serotonin and reduce anxiety. Engaging in regular exercise has been shown to increase serotonin production and release in the brain. Exercise also promotes the release of endorphins, which are known to improve mood and reduce stress.
Diet can also impact serotonin levels. Consuming foods rich in tryptophan, an amino acid that serves as a precursor to serotonin, can help increase serotonin production. Examples of tryptophan-rich foods include turkey, eggs, salmon, and nuts. Additionally, practicing stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help regulate serotonin levels and promote a sense of calmness.
What other neurotransmitters are involved in anxiety?
While serotonin is an important neurotransmitter in anxiety, it is not the only one involved. Other neurotransmitters such as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and norepinephrine also play significant roles in anxiety regulation.
GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter that helps calm the brain and reduce anxiety. It counteracts the excitatory effects of other neurotransmitters, helping to maintain a balance in brain activity. Norepinephrine, on the other hand, is involved in the body’s stress response and can contribute to anxiety when levels are dysregulated.
Understanding the complex interplay of these neurotransmitters is crucial in developing effective treatments for anxiety disorders. Medications targeting these neurotransmitter systems, such as benzodiazepines for GABA and selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) for norepinephrine, are commonly prescribed to help manage anxiety symptoms.
The Role of Serotonin (5-HT) in Impulsivity/Aggression, Anxiety/Stress and Cognition
Final Summary: The Role of Serotonin in Anxiety
In conclusion, serotonin plays a crucial role in anxiety. This neurotransmitter, often referred to as the “feel-good” chemical, helps regulate mood, emotions, and anxiety levels in the brain. When serotonin levels are imbalanced, it can lead to an increased risk of anxiety disorders.
When it comes to anxiety, serotonin acts as a natural calming agent. It helps to regulate the brain’s response to stress and anxiety-inducing situations. When serotonin levels are low, individuals may experience increased feelings of unease, worry, and panic. On the other hand, when serotonin levels are at their optimal range, it promotes a sense of calmness and emotional stability.
It’s important to note that anxiety is a complex condition influenced by various factors, and serotonin is just one piece of the puzzle. However, understanding the role of serotonin in anxiety can help us better comprehend the underlying mechanisms of this condition and explore potential treatment options.
By optimizing serotonin levels through lifestyle changes, therapy, or medication, individuals with anxiety may find relief and improved quality of life. It’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and support.
So, the next time you find yourself feeling anxious, remember the significance of serotonin in maintaining emotional balance. Take care of your mental well-being, and don’t hesitate to seek help if anxiety becomes overwhelming. Remember, you have the power to navigate your journey towards a calmer and more fulfilling life.