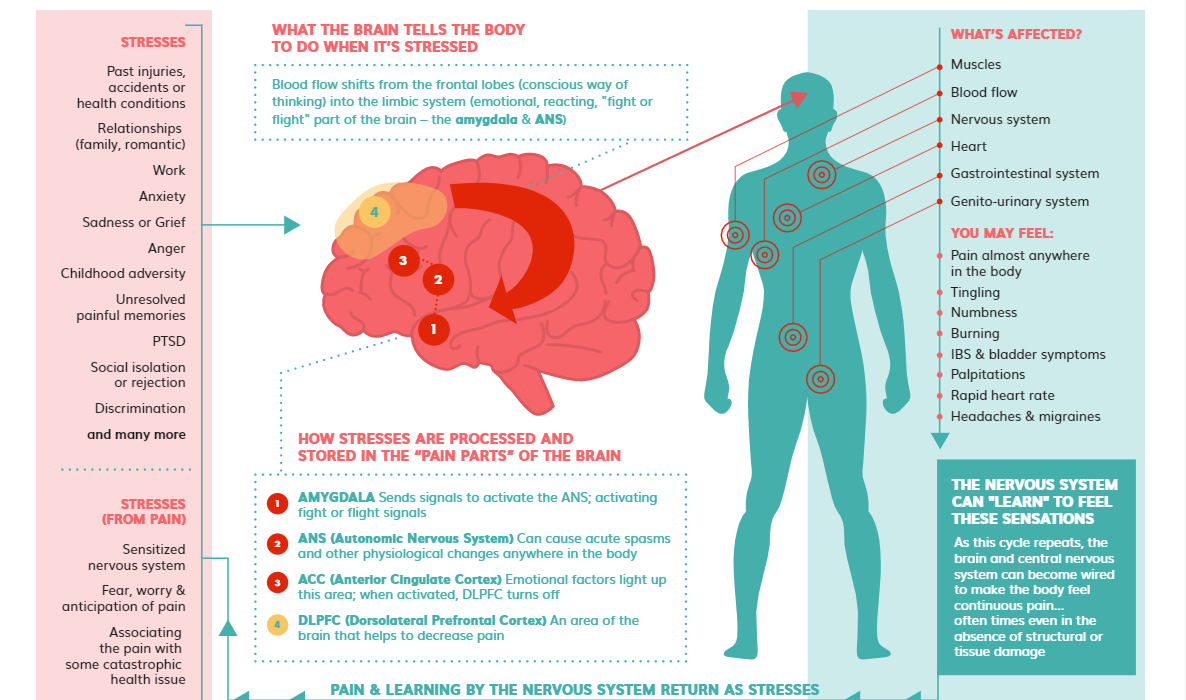
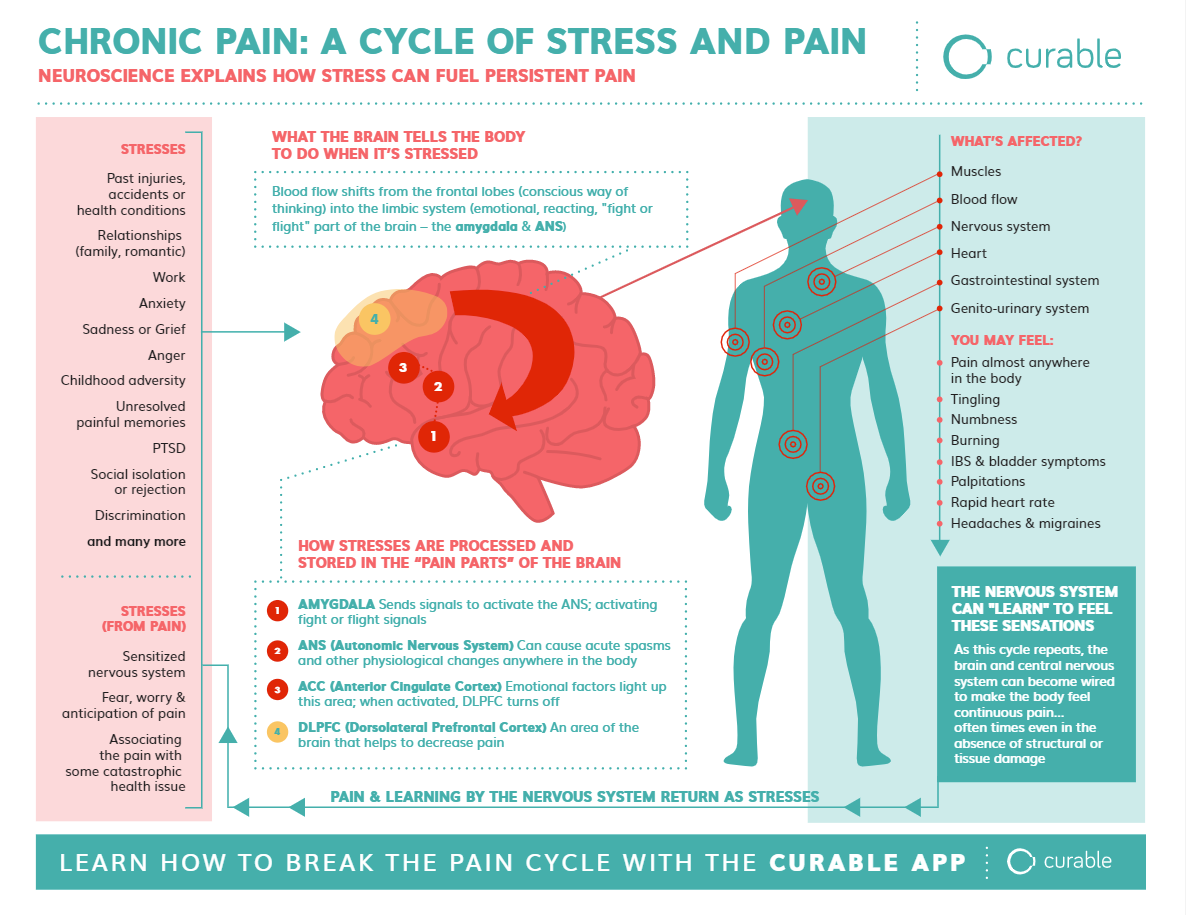
Stress and pain relief are two common experiences that many of us have encountered at some point in our lives. But have you ever wondered if there is a link between the two? Is it possible that stress could actually provide some relief from pain? Let’s delve into this intriguing topic and explore the fascinating connection between stress and pain relief.
It may seem counterintuitive, but there is growing evidence suggesting that stress can indeed have a positive impact on pain relief. When we experience stress, our bodies release a cascade of hormones, including cortisol, which is known to have anti-inflammatory properties. This natural response to stress could potentially result in reduced pain levels. So, the next time you find yourself in a stressful situation, you might just notice that your pain subsides a little. But how exactly does this phenomenon work? Let’s dive deeper into the science behind it.
Is There a Link Between Stress and Pain Relief?
Stress and pain are two common experiences that many people go through at different points in their lives. It is often said that stress can exacerbate pain, making it feel more intense and overwhelming. However, there is also evidence to suggest that stress can actually have a pain-relieving effect in certain situations. In this article, we will explore the relationship between stress and pain relief, uncovering the mechanisms behind this connection and discussing the potential benefits it can have on our overall well-being.
The Stress-Pain Connection: How Does it Work?
When we experience stress, our bodies go into a state of heightened arousal. This response triggers the release of stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline, which prepare us to face potential threats or challenges. One of the effects of these hormones is to dull our perception of pain. This is known as stress-induced analgesia, where the body’s natural painkillers, such as endorphins, are released to alleviate discomfort.
Research has shown that acute stress, such as a sudden and intense situation, can lead to a temporary reduction in pain sensitivity. For example, individuals who have undergone a stressful event, like a car accident or a medical procedure, may report feeling less pain during the immediate aftermath. This can be attributed to the body’s natural defense mechanism, which prioritizes survival and minimizes the perception of pain in high-stress situations.
The Role of Stress in Chronic Pain
While acute stress may provide temporary pain relief, the relationship between stress and chronic pain is more complex. Chronic pain refers to persistent pain that lasts for weeks, months, or even years. In this context, stress can actually worsen the experience of pain and make it more challenging to manage.
Chronic pain conditions, such as fibromyalgia or migraines, are often characterized by heightened sensitivity to pain. When individuals with these conditions experience stress, it can trigger a cascade of physiological responses that amplify their pain perception. The release of stress hormones can sensitize the pain pathways in the brain, making even minor discomfort feel more intense and overwhelming.
It’s important to note that the connection between stress and chronic pain is bidirectional. Chronic pain itself can lead to increased stress levels, creating a vicious cycle of pain and stress that can be difficult to break. Managing stress becomes crucial in these cases, as it can help reduce the overall pain experience and improve one’s quality of life.
The Benefits of Stress-Induced Analgesia
While chronic stress can exacerbate pain, there are instances where stress-induced analgesia can be beneficial. In certain situations, such as during childbirth or intense physical activity, the body’s stress response can help alleviate pain and provide a temporary sense of relief.
During childbirth, for example, the release of stress hormones can help dampen the pain sensations experienced by the mother. This natural pain relief mechanism allows women to endure the rigors of labor and delivery. Similarly, engaging in vigorous exercise can trigger the release of endorphins, which act as natural painkillers, providing a sense of euphoria and reducing discomfort.
It’s worth noting that stress-induced analgesia should not be relied upon as a long-term solution for managing chronic pain. While it may provide temporary relief, it is essential to address the underlying causes of pain and develop comprehensive strategies for pain management and stress reduction.
Tips for Managing Stress and Pain
If you are experiencing chronic pain or find that stress is exacerbating your discomfort, there are several strategies you can employ to manage both effectively. Here are some tips:
1. Practice relaxation techniques: Engage in activities such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga to promote relaxation and reduce stress levels.
2. Stay active: Regular exercise can help release endorphins, improve mood, and reduce pain perception. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable exercise regimen for your specific needs.
3. Seek social support: Share your experiences and challenges with trusted friends, family members, or support groups. Connecting with others who understand your situation can provide emotional support and practical advice.
4. Prioritize self-care: Take time for yourself and engage in activities that bring you joy and relaxation. This can include hobbies, spending time in nature, or indulging in a favorite pastime.
5. Seek professional help: If chronic pain and stress are significantly impacting your quality of life, consider consulting with a healthcare professional, such as a pain specialist or therapist. They can provide guidance and personalized treatment options to help manage your symptoms effectively.
In conclusion, the relationship between stress and pain relief is complex. While acute stress can temporarily alleviate pain, chronic stress can worsen the experience of pain and make it more challenging to manage. Understanding the mechanisms behind stress-induced analgesia and implementing strategies to effectively manage stress and pain can contribute to overall well-being and improve one’s quality of life. Remember to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment options tailored to your specific needs.
Key Takeaways: Is there a link between stress and pain relief?
- Stress can actually worsen pain symptoms in some cases.
- Reducing stress levels may help alleviate certain types of pain.
- Engaging in relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation can help manage pain.
- Positive emotions and social support can contribute to pain relief.
- It’s important to find healthy ways to cope with stress to promote overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the relationship between stress and pain relief?
Stress and pain relief are closely connected as stress has been shown to have both positive and negative effects on pain perception. When we experience stress, our bodies release hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can temporarily decrease pain sensitivity. This is known as stress-induced analgesia, where stress acts as a natural painkiller.
On the other hand, chronic stress can contribute to the development or exacerbation of pain conditions. Prolonged stress can lead to increased muscle tension, inflammation, and altered pain processing in the brain. These factors can intensify existing pain or trigger new pain sensations. Therefore, the relationship between stress and pain relief is complex and can vary depending on the individual and the specific circumstances.
Can stress actually reduce pain?
Yes, stress can sometimes reduce pain. When we experience acute stress, our bodies release endorphins and other natural pain-relieving substances, which can temporarily alleviate pain. This is often referred to as the “fight or flight” response, where the body is primed to deal with threats or danger.
However, it’s important to note that chronic stress can have the opposite effect and actually increase pain sensitivity. Prolonged stress can lead to muscle tension, inflammation, and changes in pain processing, all of which can contribute to heightened pain levels. Therefore, while stress can provide temporary pain relief in certain situations, it’s crucial to manage stress effectively to prevent the development or worsening of chronic pain conditions.
Are there any studies linking stress reduction techniques to pain relief?
Yes, several studies have found a link between stress reduction techniques and pain relief. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation have been shown to decrease stress levels and improve pain management in individuals with chronic pain.
For example, a study published in the Journal of Pain Research found that mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) significantly reduced pain intensity and improved overall well-being in patients with chronic pain. Another study published in the Journal of Behavioral Medicine showed that deep breathing exercises reduced pain sensitivity and increased pain tolerance in healthy individuals.
How does stress affect pain perception in the body?
Stress can affect pain perception in the body through various mechanisms. One way is by increasing muscle tension. When we’re stressed, our muscles tend to become tense and tight, which can exacerbate existing pain or lead to the development of new pain sensations.
Additionally, stress can influence the release of neurotransmitters and hormones in the brain, altering the way pain signals are processed. Chronic stress can disrupt the body’s natural pain-regulating systems, leading to heightened pain sensitivity and a decreased ability to manage pain effectively.
What are some effective stress management techniques for pain relief?
There are several effective stress management techniques that can help alleviate pain. Mindfulness meditation, for example, involves focusing on the present moment and calmly observing thoughts and sensations without judgment. This practice has been shown to reduce stress levels and improve pain management.
Other techniques include deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and engaging in activities that promote relaxation and pleasure, such as listening to music or spending time in nature. It’s important to find what works best for you and incorporate stress management practices into your daily routine to effectively manage pain and improve overall well-being.
Does Stress Or Anxiety Cause Pain
Final Summary: The Link Between Stress and Pain Relief
After exploring the fascinating connection between stress and pain relief, it’s clear that there is indeed a strong link between the two. While stress is often seen as a negative force, it can actually have positive effects on pain management. Studies have shown that stress-induced analgesia, or the reduction of pain perception during times of stress, is a real phenomenon that can provide much-needed relief.
When we experience stress, our bodies release endorphins, which are natural painkillers. These endorphins bind to the opioid receptors in our brain, resulting in a decreased perception of pain. Additionally, stress can also activate the body’s natural anti-inflammatory response, reducing pain and inflammation. So, in a way, stress can act as a built-in mechanism for pain relief.
However, it’s important to note that chronic or excessive stress can have detrimental effects on our overall health and well-being. While short-term stress can provide temporary pain relief, prolonged stress can lead to a variety of physical and mental health issues. Therefore, it’s crucial to find healthy and sustainable ways to manage stress in order to maintain optimal health.
In conclusion, the link between stress and pain relief is a complex and intriguing topic. While stress can provide temporary relief from pain through the release of endorphins and activation of the body’s anti-inflammatory response, it’s essential to strike a balance and effectively manage stress in the long term. By understanding this connection and adopting healthy stress management techniques, we can harness the benefits of stress-induced analgesia while safeguarding our overall well-being.