Are you tired of dealing with the constant pain and discomfort caused by carpal tunnel syndrome? Looking for effective ways to manage your pain and find some relief? Well, look no further! In this article, we will explore the best strategies and techniques to help you manage pain relief for carpal tunnel syndrome.
Carpal tunnel syndrome can be a real pain in the wrist, quite literally! It occurs when the median nerve, which runs from your forearm to your hand, becomes compressed or squeezed at the wrist. This compression can lead to a variety of symptoms, including pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand and fingers. If you’re experiencing these symptoms, it’s important to take action and find ways to alleviate the pain. So, let’s dive in and discover some effective methods for managing pain relief for carpal tunnel syndrome!
- Rest your hands: Take breaks from activities that aggravate your symptoms.
- Apply cold packs: Use ice packs to reduce inflammation and numb the area.
- Use wrist splints: Wear wrist splints at night to keep your wrists in a neutral position and relieve pressure on the median nerve.
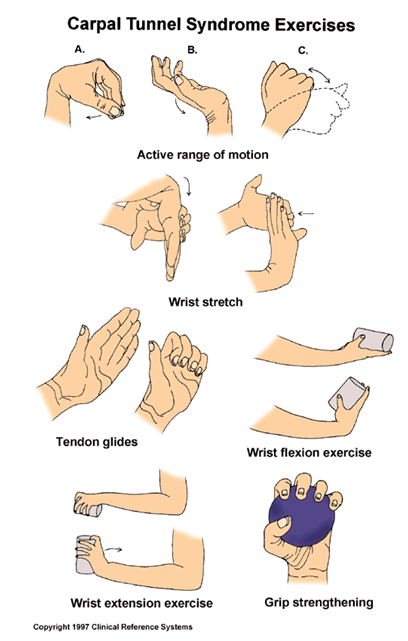
- Perform hand exercises: Stretch and strengthen the muscles in your hands and wrists to improve flexibility and reduce pain.
- Take over-the-counter pain relievers: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help alleviate pain and reduce swelling.
- Consider physical therapy: A therapist can teach you exercises and techniques to manage pain and improve function.
- Explore alternative treatments: Acupuncture, yoga, and chiropractic care may provide relief for some individuals.
Managing Pain Relief for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Comprehensive Guide
Living with carpal tunnel syndrome can be challenging, especially when the pain becomes unbearable. However, there are various strategies and treatments available to help manage and relieve the discomfort associated with this condition. In this article, we will explore effective ways to alleviate pain caused by carpal tunnel syndrome and improve your overall quality of life.
Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that affects the hand and wrist, causing pain, numbness, and tingling. It occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the hand, becomes compressed or squeezed at the wrist. This compression can be caused by a variety of factors, including repetitive hand movements, certain medical conditions, and hormonal changes.
To effectively manage pain relief for carpal tunnel syndrome, it is crucial to understand the underlying causes and triggers of the condition. By addressing these factors, you can develop a comprehensive approach to alleviate pain and promote healing.
Evaluating Your Daily Activities
One of the first steps in managing carpal tunnel syndrome pain is identifying the activities that may be exacerbating your symptoms. Take some time to evaluate your daily routine and pinpoint any repetitive hand movements or tasks that put strain on your wrists. These activities may include typing, using a computer mouse, or engaging in hobbies that require repetitive hand motions.
Once you have identified these activities, consider implementing ergonomic modifications to minimize strain on your wrists. This may include using wrist rests, adjusting the position of your keyboard or mouse, or using voice recognition software to reduce the need for excessive typing.
Seeking Professional Treatment
While self-care measures can provide temporary relief, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive treatment plan. A doctor or specialist experienced in treating carpal tunnel syndrome can evaluate your symptoms, conduct diagnostic tests, and recommend appropriate interventions.
Depending on the severity of your condition, treatment options may range from conservative measures such as wearing wrist splints and engaging in physical therapy to more invasive interventions like corticosteroid injections or surgical procedures. Your healthcare provider will work with you to determine the most suitable treatment plan based on your individual needs and preferences.
Effective Pain Relief Strategies
1. Wearing Wrist Splints
Wrist splints are often recommended as an initial treatment option for carpal tunnel syndrome. These devices help stabilize the wrist and alleviate pressure on the median nerve, reducing pain and discomfort. Wearing wrist splints at night can be particularly beneficial, as it prevents the wrists from bending and further compressing the nerve during sleep.
2. Engaging in Physical Therapy
Physical therapy exercises can help strengthen the muscles in your hand and wrist, improving flexibility and reducing pain. A physical therapist can guide you through specific exercises and stretches designed to alleviate carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms. They may also provide recommendations on lifestyle modifications and ergonomic adjustments to prevent further aggravation of your condition.
3. Exploring Alternative Therapies
Many individuals find relief from carpal tunnel syndrome pain through alternative therapies such as acupuncture, chiropractic care, or massage therapy. These treatments focus on alleviating muscle tension, improving circulation, and promoting overall relaxation. While the effectiveness of these therapies may vary from person to person, they can be worth exploring as part of a comprehensive pain management plan.
Preventing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
In addition to managing pain relief, it is essential to take proactive steps to prevent carpal tunnel syndrome from worsening or recurring. Here are some preventive measures you can incorporate into your daily routine:
1. Take Frequent Breaks
When engaging in repetitive hand movements, it is crucial to take regular breaks to rest and stretch your hands and wrists. Set a timer or use reminder apps to prompt you to take breaks throughout the day. Use these breaks to perform gentle hand and wrist stretches to relieve tension and promote blood flow.
2. Maintain Proper Ergonomics
Ensure that your workspace is set up ergonomically to minimize strain on your wrists and hands. Adjust the height of your chair, desk, and computer monitor to maintain a neutral wrist position. Invest in an ergonomic keyboard and mouse that provide proper support and alignment for your hands.
3. Strengthen Your Hand Muscles
Regularly engaging in hand and wrist exercises can help improve muscle strength and flexibility, reducing the risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome. Simple exercises like squeezing a stress ball, stretching your fingers, and performing wrist curls can be incorporated into your daily routine.
4. Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can contribute to overall well-being and potentially reduce the risk of carpal tunnel syndrome. Eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, getting regular exercise, and managing stress levels can all play a role in preventing and managing this condition.
Conclusion
Managing pain relief for carpal tunnel syndrome requires a multifaceted approach that addresses the underlying causes and incorporates various treatment strategies. By implementing ergonomic modifications, seeking professional treatment, and practicing preventive measures, you can effectively alleviate pain and improve your overall quality of life. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance on managing your carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms.
Key Takeaways: How to Manage Pain Relief for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
- Rest your hands and wrists regularly to prevent strain.
- Apply ice packs to reduce inflammation and numb the pain.
- Perform gentle stretching exercises to improve flexibility.
- Wear wrist splints or braces to provide support and relieve pressure.
- Take over-the-counter pain relievers, as recommended by your doctor.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some non-surgical methods for managing pain relief for carpal tunnel syndrome?
When it comes to managing pain relief for carpal tunnel syndrome, there are several non-surgical methods that can be effective. One such method is wearing a wrist splint, which helps to keep the wrist in a neutral position and alleviate pressure on the median nerve. Another option is to engage in regular stretching exercises for the wrist and hand, which can help to improve flexibility and reduce pain. Additionally, applying ice to the affected area can help to reduce inflammation and numb the pain temporarily.
In some cases, over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be recommended to help manage the pain associated with carpal tunnel syndrome. These medications can help to reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any medication regimen to ensure it is safe and appropriate for your specific situation.
Are there any natural remedies that can help with pain relief for carpal tunnel syndrome?
Yes, there are several natural remedies that can help with pain relief for carpal tunnel syndrome. One such remedy is practicing yoga or other forms of gentle exercise that promote flexibility and improve circulation. These exercises can help to reduce pain and stiffness in the wrist and hand. Another natural remedy is using herbal supplements such as turmeric or ginger, which have anti-inflammatory properties that can help to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
Additionally, making ergonomic adjustments to your workspace can also be beneficial in managing carpal tunnel syndrome pain. This can include using an ergonomic keyboard and mouse, adjusting the height of your chair and desk, and taking regular breaks to rest and stretch your hands and wrists. These natural remedies can complement other treatment methods and provide relief for carpal tunnel syndrome.
Can physical therapy be helpful in managing pain relief for carpal tunnel syndrome?
Physical therapy can be a valuable treatment option for managing pain relief for carpal tunnel syndrome. A physical therapist can work with you to develop a customized exercise program that targets the specific muscles and tendons affected by carpal tunnel syndrome. These exercises can help to strengthen the muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce pain and inflammation.
In addition to exercises, a physical therapist may also use techniques such as manual therapy, ultrasound, or electrical stimulation to help alleviate pain and improve mobility. They can also provide guidance on proper ergonomics and body mechanics to prevent further strain on the wrist and hand. Physical therapy can be a non-invasive and effective way to manage pain relief for carpal tunnel syndrome.
What role does lifestyle modification play in managing pain relief for carpal tunnel syndrome?
Lifestyle modification can play a significant role in managing pain relief for carpal tunnel syndrome. Making certain changes to your daily routine and habits can help to alleviate symptoms and prevent further aggravation of the condition. One important aspect of lifestyle modification is taking frequent breaks and avoiding repetitive motions that put strain on the wrist and hand.
It is also important to maintain a healthy weight, as excess weight can contribute to increased pressure on the median nerve. Engaging in regular exercise and incorporating activities that promote wrist and hand flexibility, such as yoga or tai chi, can also be beneficial. Additionally, practicing good posture and using proper ergonomics when working or performing daily tasks can help to reduce strain on the wrist and hand.
When should I consider surgical intervention for carpal tunnel syndrome?
Surgical intervention for carpal tunnel syndrome is typically considered when non-surgical methods have failed to provide sufficient pain relief and improvement in symptoms. It may also be recommended if there is evidence of nerve damage or if the condition is significantly affecting daily activities and quality of life.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if surgery is the right option for you. They will consider factors such as the severity of your symptoms, the duration of symptoms, and any underlying conditions that may affect the success of surgery. Surgical intervention for carpal tunnel syndrome can provide long-term pain relief and improved functionality, but it is a decision that should be made in collaboration with your healthcare provider.
Final Thoughts on Managing Pain Relief for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
In conclusion, finding effective pain relief for carpal tunnel syndrome is crucial for those who suffer from this condition. By incorporating a combination of lifestyle changes, ergonomic adjustments, and targeted exercises, individuals can significantly reduce their pain and improve their overall quality of life. Remember, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action for your specific situation.
Take Control of Your Pain and Regain Your Freedom
In summary, managing carpal tunnel syndrome pain requires a multifaceted approach that addresses both the underlying causes and the symptoms. By implementing the strategies outlined in this article, such as wrist splints, regular breaks, and exercises, you can take control of your pain and regain your freedom. Don’t let carpal tunnel syndrome hold you back any longer. With the right tools and techniques, you can find relief and continue pursuing the activities you love. Remember, it’s never too late to start taking care of yourself and seeking the pain relief you deserve.