Have you ever wondered about the relationship between anxiety and depression? Well, let’s dive into this intriguing topic and explore the intricate connection between these two mental health conditions. Anxiety and depression often go hand in hand, like two peas in a pod. They can intertwine and amplify each other’s effects, creating a complex web of emotions and challenges. So, what exactly is the relationship between anxiety and depression, and how do they influence one another? Let’s unravel this mystery together.
When it comes to anxiety and depression, it’s like a chicken and egg scenario – it’s hard to determine which came first. Anxiety can be a precursor to depression, as the constant worry, fear, and apprehension can wear a person down, leading to feelings of sadness and hopelessness. On the other hand, depression can also give rise to anxiety, as the lack of motivation, energy, and joy can make everyday tasks seem overwhelming, triggering anxious thoughts and feelings. It’s a vicious cycle that can be challenging to break free from.
Understanding the relationship between anxiety and depression is crucial for both individuals struggling with these conditions and those who want to support them. By shedding light on this topic, we can foster empathy, compassion, and knowledge, ultimately leading to better mental health care and a more supportive society. So, let’s delve deeper into the intricate dance of anxiety and depression and discover how they intertwine and impact our lives.
**What is the Relationship Between Anxiety and Depression?**
Anxiety and depression are two mental health disorders that often go hand in hand. Many individuals who struggle with anxiety also experience symptoms of depression, and vice versa. While these two conditions are distinct, they share similarities and can influence one another. Understanding the relationship between anxiety and depression is important for individuals, as well as for healthcare professionals, in order to provide effective treatment and support.
**Understanding Anxiety and Depression**
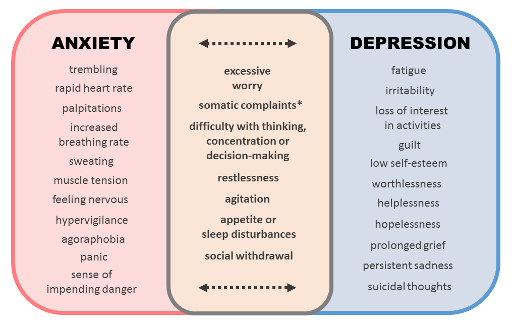
Anxiety is characterized by excessive worry, fear, and apprehension. It can manifest in various forms such as generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobias. Depression, on the other hand, is characterized by feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest in activities. Major depressive disorder, persistent depressive disorder, and postpartum depression are some of the different types of depression that exist.
**The Overlapping Symptoms**
While anxiety and depression are distinct disorders, they often share common symptoms. For example, individuals with both anxiety and depression may experience persistent feelings of sadness, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. They may also have trouble sleeping, experience changes in appetite, and feel fatigued. Additionally, both anxiety and depression can lead to physical symptoms such as headaches, stomachaches, and muscle tension. Understanding these shared symptoms is essential for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
**The Vicious Cycle**
Anxiety and depression can perpetuate a vicious cycle, with each disorder exacerbating the other. For instance, anxiety can lead to increased feelings of stress and worry, which can contribute to the development or worsening of depressive symptoms. On the other hand, depression can lead to decreased motivation, low energy levels, and a lack of interest in activities, which can increase feelings of anxiety and contribute to the development of anxiety disorders. This cycle can make it challenging for individuals to break free from the grip of both anxiety and depression.
**The Role of Genetics and Biology**
Both genetics and biology play a role in the development of anxiety and depression. Research suggests that individuals with a family history of these disorders may be more susceptible to developing them. Additionally, imbalances in certain brain chemicals, such as serotonin and dopamine, have been associated with the development of anxiety and depression. Understanding these biological factors can help inform treatment approaches, such as medication and other interventions.
**Treatment Approaches**
Treating anxiety and depression often involves a multi-faceted approach. Therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can be effective in helping individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns and develop coping strategies. Medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), may also be prescribed to help regulate brain chemicals and alleviate symptoms. In some cases, a combination of therapy and medication may be recommended. Additionally, lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, healthy eating, and stress management techniques, can also play a role in managing symptoms.
**Support and Self-Care**
Having a strong support system is crucial for individuals dealing with anxiety and depression. Friends, family, and support groups can provide understanding, empathy, and encouragement. Engaging in self-care activities, such as practicing mindfulness, engaging in hobbies, and taking time for relaxation, can also help manage symptoms. It’s important for individuals to prioritize their mental health and engage in activities that bring them joy and a sense of peace.
**Seeking Professional Help**
If you or someone you know is struggling with anxiety and depression, it’s important to seek professional help. A mental health professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and develop a personalized treatment plan. Remember, you are not alone in your journey, and there is support and help available to you.
**In Summary**
The relationship between anxiety and depression is complex and interconnected. While they are distinct disorders, they often coexist and can influence one another. Understanding the shared symptoms, the vicious cycle, and the role of genetics and biology can help inform treatment approaches. Seeking professional help, building a support system, and engaging in self-care activities are essential steps in managing anxiety and depression. Remember, there is hope, and with the right support and treatment, it is possible to live a fulfilling and meaningful life.
Key Takeaways: The Relationship Between Anxiety and Depression
- Anxiety and depression often coexist, with many individuals experiencing symptoms of both conditions.
- Anxiety and depression share common risk factors, such as genetics, brain chemistry, and life events.
- Having anxiety can increase the risk of developing depression, and vice versa.
- Both anxiety and depression can have similar symptoms, including persistent sadness, loss of interest, and difficulty concentrating.
- Treatment for anxiety and depression may involve a combination of therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1: What are the common symptoms of anxiety and depression?
Anxiety and depression are two different mental health conditions, but they often occur together and share similar symptoms. Common symptoms of anxiety include excessive worry, restlessness, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and physical manifestations such as tense muscles and trouble sleeping. On the other hand, depression is characterized by feelings of sadness, loss of interest or pleasure in activities, changes in appetite or weight, fatigue, and thoughts of self-harm or suicide.
It is important to note that the severity and duration of these symptoms can vary from person to person. If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it is recommended to seek professional help for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Question 2: How are anxiety and depression related?
Anxiety and depression often coexist and can influence each other. Research suggests that individuals with anxiety disorders are at a higher risk of developing depression, and vice versa. The relationship between anxiety and depression is complex and can vary from person to person.
One possible explanation for their co-occurrence is that they share common underlying biological and genetic factors. Additionally, stressful life events, trauma, and chronic health conditions can contribute to the development of both anxiety and depression. It is also important to consider that the symptoms of one condition can worsen or trigger symptoms of the other, leading to a cycle of anxiety and depression.
Question 3: Can anxiety lead to depression?
Yes, anxiety can potentially lead to depression. Anxiety disorders, especially when left untreated, can significantly impact a person’s daily functioning and quality of life. The persistent worry, fear, and uncertainty associated with anxiety can be overwhelming and exhausting, leading to feelings of hopelessness and despair.
Moreover, the constant anticipation of negative outcomes and the avoidance of certain situations or activities due to anxiety can limit a person’s experiences and social interactions, which can contribute to feelings of isolation and sadness. It is essential to seek professional help to manage anxiety effectively and prevent it from progressing into depression.
Question 4: How are anxiety and depression treated?
Treatment for anxiety and depression typically involves a combination of therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a commonly used therapy approach that helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with anxiety and depression.
Medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) may be prescribed to help regulate mood and reduce symptoms. Additionally, lifestyle changes like regular exercise, stress management techniques, and healthy sleep habits can also play a crucial role in managing anxiety and depression.
Question 5: Can anxiety and depression be prevented?
While it may not be possible to prevent anxiety and depression entirely, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk and promote mental well-being. Developing healthy coping mechanisms, such as practicing mindfulness and relaxation techniques, maintaining a balanced lifestyle, and seeking support from loved ones, can help manage stress and prevent the onset of anxiety and depression.
Early intervention is also crucial. If you notice persistent symptoms of anxiety or depression, it is important to seek professional help promptly. Mental health professionals can provide appropriate guidance, support, and treatment options to address these conditions effectively.
Relationship Between Anxiety and Depression
Final Thoughts: Understanding the Connection Between Anxiety and Depression
When it comes to the relationship between anxiety and depression, it’s important to recognize that these two mental health conditions often go hand-in-hand. They are like two sides of the same coin, intricately intertwined and influencing each other in complex ways. While anxiety and depression are distinct disorders, they share common symptoms and underlying factors that contribute to their coexistence.
One key aspect to consider is that anxiety can often be a precursor to depression. When someone experiences chronic anxiety, the constant worry, fear, and stress can take a toll on their mental well-being. This prolonged state of heightened anxiety can deplete their emotional resources, leaving them vulnerable to developing depression. On the other hand, depression can also lead to anxiety. When someone feels down, hopeless, and lacking motivation, they may start to worry about the future and become anxious about their circumstances.
Additionally, anxiety and depression share common biological and environmental factors. Both conditions can be influenced by genetic predispositions, imbalances in brain chemicals, and traumatic life experiences. These factors can contribute to the development of anxiety and depression and make it more likely for someone to experience both simultaneously.
Understanding the relationship between anxiety and depression can help us approach mental health treatment more effectively. By recognizing the interconnected nature of these conditions, healthcare professionals can develop comprehensive treatment plans that address both anxiety and depression. Whether it involves therapy, medication, lifestyle changes, or a combination of approaches, addressing both conditions simultaneously can lead to better outcomes for individuals struggling with their mental well-being.
Remember, if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of anxiety or depression, it’s important to seek professional help. Mental health matters, and with the right support, it is possible to navigate the challenges and find a path towards healing and well-being.