Ever feel like you’re constantly on edge, your heart racing, and your mind spinning with worry? Or maybe you find yourself overwhelmed and exhausted, juggling a million tasks and responsibilities? It’s no secret that modern life can be stressful, but what if I told you that there’s a difference between stress and anxiety? That’s right, my friend! In this article, we’re going to dive into the fascinating world of emotions and explore the dissimilarities between anxiety and stress. So, grab your favorite beverage, sit back, and let’s embark on this enlightening journey together!
When it comes to anxiety and stress, many people use these terms interchangeably. But is there really no difference between the two? Well, hold your horses, because there’s more to it than meets the eye. Anxiety and stress may share some similarities, like making your heart race and leaving you feeling overwhelmed, but they actually originate from different sources. So, if you’re ready to unravel the mysteries of these emotions and gain a deeper understanding of your own mental well-being, then let’s get started!
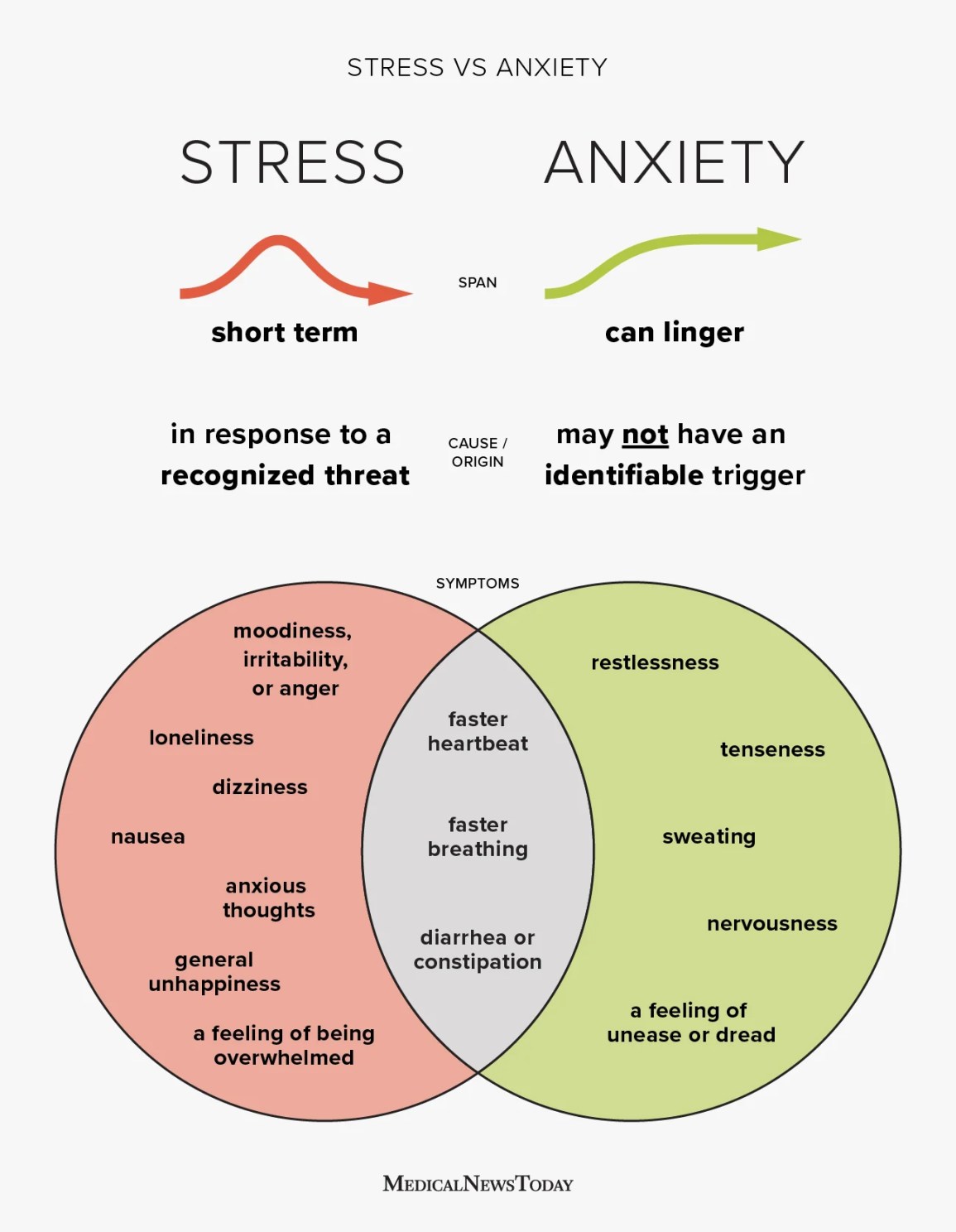
Understanding the Difference Between Anxiety and Stress
Anxiety and stress are two terms that are often used interchangeably, but they actually have distinct meanings and effects on our well-being. While both can be overwhelming and have negative impacts on our lives, it is important to understand the differences between them in order to effectively manage and address these challenges. In this article, we will explore the disparities between anxiety and stress, their causes, symptoms, and potential coping strategies.
What is Anxiety?
Anxiety is a psychological and physiological response to perceived threats or dangers. It is a normal human emotion that everyone experiences at some point in their lives. However, for some individuals, anxiety can become persistent and excessive, interfering with their daily functioning and overall quality of life.
Anxiety is characterized by feelings of unease, worry, and fear. It can manifest in various forms, such as generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, or specific phobias. Common symptoms of anxiety include restlessness, irritability, difficulty concentrating, muscle tension, and sleep disturbances. These symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s ability to function in social, occupational, or academic settings.
The Causes of Anxiety
Anxiety can have various causes, including genetic factors, brain chemistry imbalances, environmental stressors, and traumatic experiences. Certain life events, such as job loss, relationship issues, or financial difficulties, can also trigger or exacerbate anxiety symptoms. Additionally, individuals with a family history of anxiety disorders may be more prone to developing anxiety themselves.
It is important to note that anxiety is not a sign of weakness or personal failure. It is a complex condition that can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or background. Seeking professional help and support is crucial for managing anxiety and improving overall well-being.
Understanding Stress
Stress, on the other hand, is a physiological and psychological response to external pressures or demands. It is a normal part of life and can sometimes be beneficial, motivating us to take action and meet deadlines. However, prolonged or excessive stress can have detrimental effects on our physical and mental health.
Stress can be triggered by a wide range of factors, including work-related pressures, relationship difficulties, financial strain, or major life changes. It can manifest in both acute and chronic forms. Acute stress occurs in response to immediate threats or challenges, while chronic stress is ongoing and persists over an extended period.
The Effects of Stress
When we experience stress, our bodies release stress hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, which prepare us for a “fight or flight” response. This physiological reaction can lead to increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and heightened alertness. In the short term, these responses can help us cope with challenges. However, chronic stress can lead to long-term health problems, including cardiovascular issues, weakened immune system, and mental health disorders.
It is essential to recognize the signs of stress, which can include fatigue, irritability, difficulty sleeping, changes in appetite, and difficulty concentrating. By identifying these symptoms, individuals can take proactive steps to manage stress and mitigate its negative impact on their well-being.
Managing Anxiety and Stress
While anxiety and stress may have different causes and effects, there are several strategies that can help individuals effectively manage both conditions. These include:
1. Seeking professional help: Consulting with a mental health professional, such as a therapist or counselor, can provide invaluable support and guidance in managing anxiety and stress. They can help individuals develop coping mechanisms, explore underlying causes, and provide evidence-based treatments.
2. Practicing relaxation techniques: Engaging in relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga, can help reduce anxiety and stress levels. These techniques promote a sense of calmness and help individuals regain control over their emotions.
3. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: Prioritizing self-care activities, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and sufficient sleep, can significantly contribute to managing anxiety and stress. Incorporating relaxation activities, such as reading, listening to music, or spending time in nature, can also be beneficial.
4. Building a support network: Connecting with supportive friends, family members, or support groups can provide a sense of belonging and understanding. Sharing experiences and seeking emotional support can alleviate feelings of isolation and help individuals navigate their anxiety and stress.
5. Setting boundaries and managing time: Learning to say no, setting realistic goals, and practicing effective time management can reduce feelings of overwhelm and prevent excessive stress. Prioritizing self-care and creating a balanced lifestyle can contribute to overall well-being.
By implementing these strategies, individuals can take proactive steps towards managing anxiety and stress, improving their mental health, and enhancing their overall quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, anxiety and stress are distinct yet interconnected experiences that can significantly impact our well-being. Understanding the differences between them can help individuals recognize their symptoms, seek appropriate support, and implement effective coping strategies. By managing anxiety and stress, individuals can enhance their overall mental health and lead more fulfilling lives.
Key Takeaways: What is the difference between anxiety and stress?
- Anxiety is a feeling of fear, worry, or unease, while stress is the body’s response to a demand or pressure.
- Anxiety is often related to specific triggers or situations, while stress can be caused by various factors.
- Anxiety can be chronic and ongoing, while stress can be temporary or short-term.
- Anxiety can lead to physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat or trouble breathing, while stress can cause headaches or muscle tension.
- Managing anxiety involves relaxation techniques and therapy, while managing stress can involve time management and self-care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main differences between anxiety and stress?
While anxiety and stress are often used interchangeably, they are not the same thing. Here are the main differences between the two:
Anxiety is a psychological condition characterized by excessive worry, fear, and apprehension. It is often accompanied by physical symptoms such as restlessness, difficulty concentrating, and muscle tension. Anxiety is typically a chronic condition that persists over time and can interfere with daily functioning.
On the other hand, stress is a response to a specific event or situation that is perceived as challenging or threatening. It is a normal part of life and can be caused by various factors such as work pressure, relationship issues, or financial problems. While stress can also cause physical symptoms, it is usually temporary and subsides once the stressor is removed or managed.
How do anxiety and stress affect the body?
Anxiety and stress can both have significant effects on the body. When a person experiences anxiety, the body’s stress response is activated, leading to the release of stress hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline. This can result in increased heart rate, rapid breathing, and heightened alertness.
Chronic anxiety can have long-term effects on the body, including an increased risk of developing health problems such as cardiovascular disease, gastrointestinal issues, and weakened immune function. It can also contribute to the development of mental health disorders such as depression.
Stress, on the other hand, can also have physical effects on the body. It can lead to symptoms such as headaches, muscle tension, and digestive problems. Prolonged or chronic stress can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to illness and disease.
Can stress cause anxiety?
While stress and anxiety are related, stress itself does not directly cause anxiety. However, chronic or prolonged stress can increase the risk of developing an anxiety disorder. When a person is constantly exposed to stressors without adequate coping mechanisms, it can lead to feelings of overwhelm and anxiety.
Stressful life events, such as the loss of a loved one or financial difficulties, can trigger or exacerbate anxiety symptoms in individuals who are already predisposed to anxiety. It is important to manage stress effectively to prevent it from escalating into chronic anxiety.
How are anxiety and stress treated?
Treatment for anxiety and stress can vary depending on the severity of symptoms and individual needs. Common treatment options include:
1. Therapy: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is often used to help individuals manage anxiety and stress. It focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to anxiety. Other types of therapy, such as relaxation techniques and exposure therapy, may also be beneficial.
2. Medication: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage symptoms of anxiety or stress. Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications are commonly used to regulate brain chemistry and reduce symptoms.
3. Lifestyle changes: Adopting healthy lifestyle habits can also help reduce anxiety and stress. This may include regular exercise, practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation, getting enough sleep, and maintaining a balanced diet.
When should I seek professional help for anxiety or stress?
If you are experiencing persistent or severe symptoms of anxiety or stress that are interfering with your daily life, it is recommended to seek professional help. A mental health professional can assess your symptoms, provide a diagnosis, and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Other signs that indicate it may be time to seek help include difficulty functioning at work or school, relationship problems, frequent panic attacks, substance abuse, or suicidal thoughts. Remember, seeking help is a sign of strength, and there are effective treatments available to help you manage anxiety and stress.
What’s the Difference Between Stress and Anxiety?
Final Thoughts on the Difference Between Anxiety and Stress
After exploring the nuances of anxiety and stress, it is clear that these two terms are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct differences. While stress is a response to external pressures and demands, anxiety is a more internalized feeling of unease and apprehension. Stress can be a normal part of life, whereas anxiety is often more persistent and can have a debilitating impact on one’s daily functioning.
Understanding the difference between anxiety and stress is crucial for developing effective coping strategies and seeking appropriate support. It’s important to recognize that stress can be managed through lifestyle changes, time management, and relaxation techniques. On the other hand, anxiety might require professional help, such as therapy or medication, to alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.
In conclusion, while stress and anxiety are both part of the human experience, they are not the same. By recognizing the distinctions between the two, individuals can better navigate their emotions, seek appropriate help when needed, and lead more balanced and fulfilling lives. Remember, it’s normal to experience stress, but when anxiety becomes overwhelming, it’s important to reach out for support and take steps towards finding peace of mind.