Sleep is a vital part of our daily lives, but have you ever wondered what happens to your body when you sleep? Well, let me introduce you to the fascinating world of sleep cycles! So, what is a sleep cycle, you ask? A sleep cycle refers to the process your body goes through while you snooze, consisting of various stages that repeat throughout the night. Understanding sleep cycles is key to optimizing your rest and waking up feeling refreshed and rejuvenated.
During a typical sleep cycle, your body goes through four distinct stages: NREM Stage 1, NREM Stage 2, NREM Stage 3, and REM sleep. NREM stands for non-rapid eye movement, while REM refers to rapid eye movement. In the initial stages of sleep, you enter NREM Stage 1, where you drift in and out of slumber and can be easily awakened. As you progress into NREM Stage 2, your body temperature drops, and your heart rate and breathing become more regular. Deep sleep, or NREM Stage 3, is where the magic happens. This is the stage where your body repairs and regenerates, promoting physical recovery and growth. Finally, we have REM sleep, which is when your brain becomes highly active, and you experience vivid dreams. This stage is crucial for cognitive function and emotional well-being.
Now that you have a brief overview of what a sleep cycle entails, let’s dive deeper into each stage and explore the incredible ways in which your body and mind rejuvenate during the night. Get ready to uncover the secrets of a good night’s sleep and discover how to make the most out of your slumber!
Understanding Sleep Cycles: A Comprehensive Guide
Sleep is a fundamental aspect of our daily lives, but have you ever wondered what goes on in our bodies while we sleep? The answer lies in understanding sleep cycles. Sleep cycles refer to the patterns of brain activity and bodily functions that occur during different stages of sleep. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of sleep cycles, exploring the different stages and their significance in achieving restful and rejuvenating sleep.
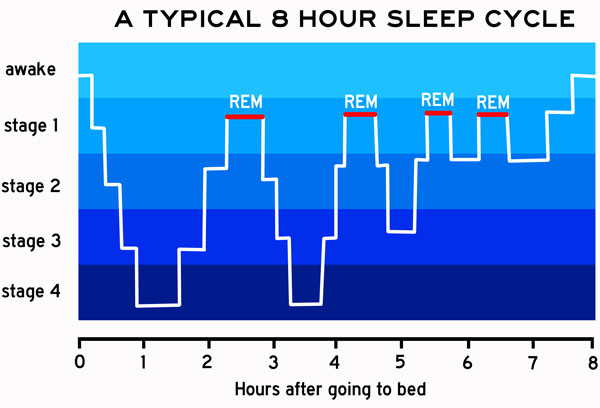
The Basics of Sleep Cycles
Sleep cycles are composed of four distinct stages: stages 1, 2, 3, and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. These stages are not linear but rather occur in a cyclical fashion throughout the night. Each cycle typically lasts around 90 minutes, with individuals experiencing multiple cycles during a night’s sleep. As the night progresses, the duration of REM sleep increases while the earlier stages become shorter. This cyclical pattern allows the brain and body to undergo essential processes, such as memory consolidation and physical restoration.
During stage 1 of the sleep cycle, also known as light sleep, individuals are in a transitional state between wakefulness and sleep. This stage is characterized by a decrease in brain activity, muscle relaxation, and occasional muscle twitches. It is relatively easy for individuals to be awakened during this stage, and they may not even realize they were asleep.
The Importance of Stage 1 Sleep
Although stage 1 sleep is brief and often overlooked, it plays a crucial role in the overall sleep cycle. This initial stage allows the body to relax and prepare for deeper sleep stages. Additionally, stage 1 sleep contributes to the restoration of mental and physical energy, promoting a sense of well-being upon waking.
Moving on to stage 2 of the sleep cycle, the body transitions into a deeper state of sleep. Brain activity slows down, and eye movement ceases. During this stage, sleep spindles and K-complexes may occur. Sleep spindles are bursts of rhythmic brain activity that help suppress external stimuli, while K-complexes are large, slow brain waves that provide a protective mechanism against potential disturbances.
The Significance of Stage 2 Sleep
Stage 2 sleep is characterized by an increase in sleep spindles and K-complexes, making it more challenging to wake individuals during this stage. This deeper sleep stage supports memory consolidation, aiding in the retention of new information and the integration of experiences into long-term memory. Additionally, stage 2 sleep promotes overall physical recovery, allowing the body to repair and rejuvenate.
Moving into the third stage of the sleep cycle, also known as deep sleep or slow-wave sleep (SWS), the body reaches its most restorative state. This stage is characterized by the presence of slow brain waves called delta waves. It is more challenging to wake individuals during this stage, and if awakened, they may feel disoriented or groggy.
The Benefits of Deep Sleep
Deep sleep is essential for physical restoration and growth. During this stage, the body releases growth hormone, which aids in tissue repair, muscle growth, and overall development. Deep sleep also plays a vital role in immune function, strengthening the body’s defenses against infections and diseases. Furthermore, this stage of sleep contributes to cognitive processes, such as learning and problem-solving.
Finally, we have the REM sleep stage, which is characterized by rapid eye movements and heightened brain activity. This stage is often associated with vivid dreaming. During REM sleep, the brain becomes highly active, resembling wakefulness. However, the body undergoes temporary paralysis, known as REM atonia, to prevent individuals from acting out their dreams.
The Role of REM Sleep
REM sleep is crucial for cognitive function and emotional well-being. It is during this stage that the brain consolidates and processes information, enhancing learning and memory retention. REM sleep also plays a significant role in regulating mood and emotions, with a deficiency in REM sleep linked to increased irritability and emotional instability.
In conclusion, sleep cycles are composed of four stages, including stage 1, stage 2, deep sleep, and REM sleep. Each stage serves a unique purpose in promoting restful sleep and supporting various bodily functions. Understanding sleep cycles allows us to appreciate the importance of quality sleep and the impact it has on our overall health and well-being. So, make it a priority to prioritize a consistent sleep schedule and create an environment conducive to a good night’s rest.
Key Takeaways: What is a Sleep Cycle?
- A sleep cycle is a recurring pattern of sleep stages that your body goes through during the night.
- Each sleep cycle typically lasts around 90 minutes.
- A complete sleep cycle consists of four stages: NREM Stage 1, NREM Stage 2, NREM Stage 3, and REM sleep.
- Different stages of the sleep cycle serve different purposes for physical and mental restoration.
- Understanding your sleep cycle can help you optimize your sleep quality and wake up feeling refreshed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about sleep cycles:
Q: What happens during a sleep cycle?
During a sleep cycle, your body goes through different stages of sleep. The cycle typically consists of four stages: NREM stage 1, NREM stage 2, NREM stage 3, and REM sleep. In NREM stage 1, you are in a light sleep and can be easily awakened. In NREM stage 2, your body temperature drops and your heart rate slows down. NREM stage 3 is known as deep sleep, where your muscles relax and tissue growth and repair occur. REM sleep is the stage where most dreaming occurs and your brain becomes more active.
Throughout the night, you go through multiple sleep cycles, with each cycle lasting about 90 minutes. These cycles are important for restorative sleep and help to regulate various bodily functions.
Q: How long does a sleep cycle last?
A sleep cycle typically lasts about 90 minutes. During this time, you go through all the stages of sleep, including NREM stages 1, 2, and 3, as well as REM sleep. The length of each stage within the sleep cycle may vary, with NREM stage 2 being the longest stage. It’s important to complete multiple sleep cycles in order to feel refreshed and rested upon waking up.
If you wake up in the middle of a sleep cycle, you may feel groggy and disoriented. This is why it’s recommended to try to wake up at the end of a sleep cycle, when you are in a lighter stage of sleep.
Q: How many sleep cycles do I need?
The number of sleep cycles you need depends on your individual sleep needs. Most adults require around 7-9 hours of sleep per night, which typically translates to 4-6 complete sleep cycles. However, some individuals may need more or less sleep depending on factors such as age, activity level, and overall health.
It’s important to listen to your body and prioritize getting enough sleep to ensure optimal functioning during the day. If you consistently feel tired or have trouble falling asleep, it may be helpful to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if there are any underlying sleep issues.
Q: Can sleep cycles be disrupted?
Yes, sleep cycles can be disrupted for various reasons. Factors such as stress, caffeine intake, irregular sleep schedule, and certain medical conditions can disrupt the normal progression of sleep cycles. Disruptions to sleep cycles can result in poor sleep quality, daytime sleepiness, and difficulty concentrating.
Establishing a consistent sleep routine, creating a sleep-friendly environment, and practicing good sleep hygiene can help promote regular sleep cycles and improve sleep quality. If you continue to experience disruptions to your sleep, it may be beneficial to seek guidance from a healthcare professional.
Q: How can I improve my sleep cycles?
There are several strategies you can try to improve your sleep cycles:
1. Stick to a consistent sleep schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends.
2. Create a sleep-friendly environment: Make sure your bedroom is cool, dark, and quiet. Use comfortable bedding and pillows.
3. Practice good sleep hygiene: Avoid caffeine and electronic devices before bedtime, establish a relaxing bedtime routine, and limit daytime napping.
4. Manage stress: Incorporate stress management techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, into your daily routine.
By implementing these strategies, you can improve the quality of your sleep and support healthy sleep cycles.
Stages of Sleep – non-REM, REM, Sleep Studies
Final Summary: Understanding the Fascinating World of Sleep Cycles
So, now you have a good grasp on what a sleep cycle is and how it impacts our overall sleep quality. Sleep cycles are like the intricate dance that our bodies and brains perform every night, ensuring that we get the rest we need to function at our best. From the initial light sleep stage to the deep sleep phase and the REM sleep stage, each cycle plays a crucial role in rejuvenating our bodies and minds.
By optimizing our sleep cycles, we can enhance the quality of our sleep and wake up feeling refreshed and energized. So, how can we do that? Well, there are a few things you can try. First, establish a consistent sleep schedule to regulate your body’s internal clock. Next, create a sleep-friendly environment by making sure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool. Additionally, practicing relaxation techniques before bed can help calm your mind and prepare it for a restful night’s sleep.
Remember, everyone’s sleep cycles are unique, so it’s important to listen to your body and identify what works best for you. By understanding the fascinating world of sleep cycles and making small adjustments to improve the quality of your sleep, you can unlock the full potential of a good night’s rest. So go ahead, embrace the power of sleep and let your body and mind reap the benefits of a well-rested life. Sweet dreams!


