If you’ve ever found yourself feeling excessively tired during the day or experiencing sudden bouts of sleepiness, you might be wondering, “What are the symptoms of narcolepsy?” Well, my friend, you’ve come to the right place! In this article, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of narcolepsy and explore its various symptoms that can affect individuals who have this sleep disorder.
Narcolepsy, a neurological condition that affects the brain’s ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles, is often characterized by a range of symptoms that can disrupt daily life. One of the hallmark signs of narcolepsy is excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS), where individuals feel an overwhelming urge to sleep during the day, regardless of how much sleep they’ve had at night. This can lead to sudden and uncontrollable episodes of falling asleep, which can be quite inconvenient and even dangerous in certain situations. But that’s not all! Narcolepsy can also manifest in other ways, such as cataplexy, a sudden loss of muscle tone triggered by strong emotions like laughter or surprise. Imagine having a good laugh with friends and suddenly your legs turn to jelly! It can be quite a spectacle, but not the most pleasant experience. Other symptoms may include sleep paralysis, hallucinations, and disrupted nighttime sleep.
So, if you’ve been wondering about the symptoms of narcolepsy, buckle up and get ready for an enlightening journey as we dive deeper into this intriguing sleep disorder. We’ll explore each symptom in detail, offering insights and tips for managing them effectively. So, grab a cup of coffee, stay awake, and let’s uncover the fascinating world of narcolepsy together!
Understanding Narcolepsy: What are the Symptoms?
Narcolepsy is a chronic neurological disorder that affects the brain’s ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles. It is characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden, uncontrollable episodes of falling asleep. While the exact cause of narcolepsy is unknown, researchers believe it may be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
The Main Symptoms of Narcolepsy
Narcolepsy is often marked by a variety of symptoms that can significantly impact a person’s daily life. Here are the main symptoms of narcolepsy:
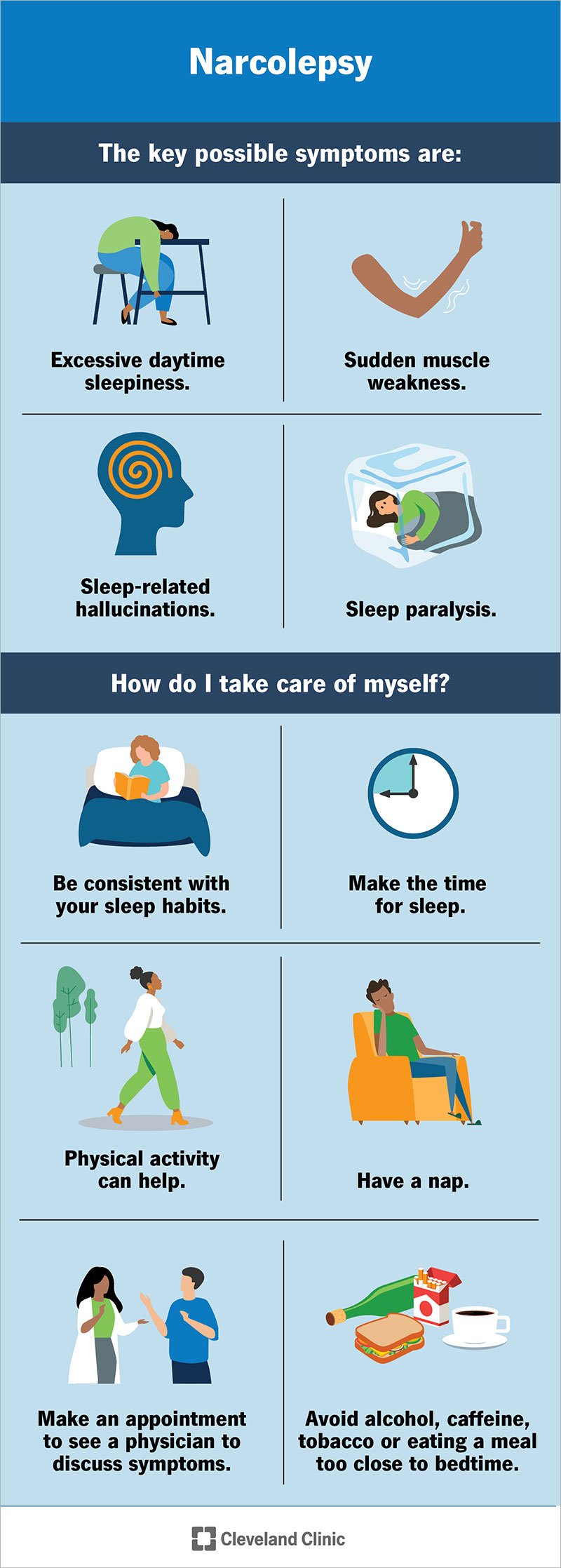
1. Excessive Daytime Sleepiness (EDS): This is the most common symptom of narcolepsy. People with narcolepsy experience an overwhelming and persistent need to sleep during the day, regardless of how much sleep they’ve had at night. They may struggle to stay awake and may unintentionally fall asleep in inappropriate situations, such as during a conversation or while driving.
2. Cataplexy: Cataplexy is a sudden loss of muscle tone triggered by strong emotions, such as laughter, anger, or surprise. During a cataplectic episode, the person may experience muscle weakness or complete paralysis, leading to a temporary inability to move or speak. Cataplexy can range from mild, with only a slight drooping of facial muscles, to severe, causing a complete collapse.
The Impact of Narcolepsy on Daily Life
Living with narcolepsy can be challenging and often affects various aspects of a person’s life. Here are some ways narcolepsy can impact daily life:
1. Work and Education: Excessive daytime sleepiness can make it difficult to stay focused and alert at work or school. People with narcolepsy may struggle to concentrate, which can affect their productivity and overall performance.
2. Relationships: Narcolepsy can strain relationships, as the excessive sleepiness and sudden sleep attacks can make it challenging to engage in activities and spend quality time with loved ones. The unpredictability of narcoleptic symptoms may also lead to misunderstandings or frustration.
3. Emotional Well-being: Coping with narcolepsy can take a toll on a person’s emotional well-being. The constant fatigue and limited ability to participate in everyday activities may lead to feelings of frustration, sadness, or isolation.
Other Symptoms of Narcolepsy
In addition to excessive daytime sleepiness and cataplexy, narcolepsy may also present with other symptoms that can further impact a person’s quality of life. These include:
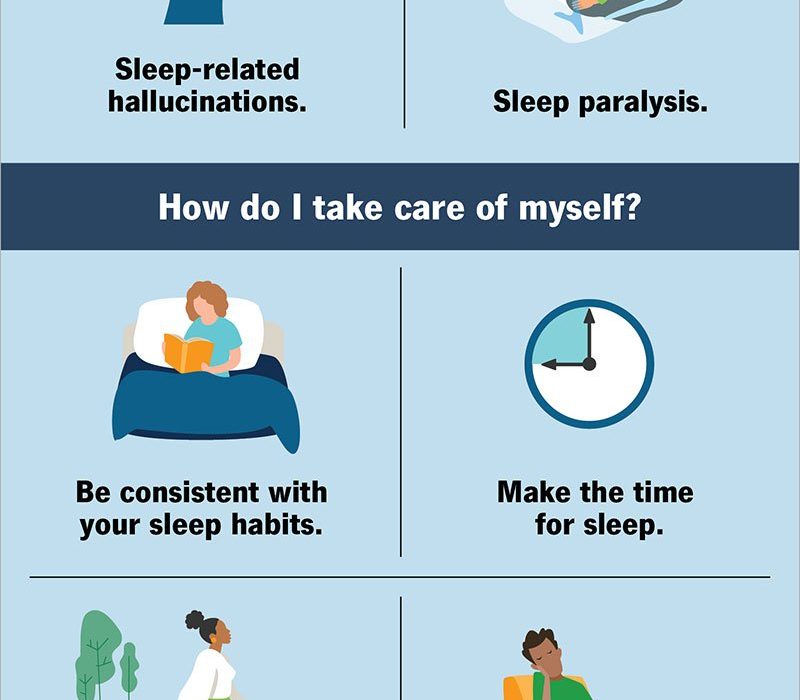
1. Sleep Paralysis: Sleep paralysis is a temporary inability to move or speak while falling asleep or waking up. It can be accompanied by vivid hallucinations and a sense of pressure on the chest. Sleep paralysis can be distressing, but it is generally harmless and lasts only a few seconds to a few minutes.
2. Hypnagogic Hallucinations: These hallucinations occur when falling asleep or waking up and can be vivid and often frightening. People with narcolepsy may see, hear, or feel things that are not actually there.
3. Fragmented Nighttime Sleep: Narcolepsy can disrupt the normal sleep pattern, causing frequent awakenings throughout the night. This fragmented sleep can lead to daytime sleepiness and a decreased ability to feel rested.
Impact on Mental Health
Living with the symptoms of narcolepsy can have a significant impact on a person’s mental health. The constant fatigue and challenges associated with managing the disorder can contribute to feelings of depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem. Seeking support from healthcare professionals and connecting with support groups can be beneficial for managing the emotional impact of narcolepsy.
Diagnosing Narcolepsy
If you suspect you may have narcolepsy, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional. A diagnosis of narcolepsy typically involves a thorough evaluation of symptoms, medical history, and sleep patterns. In some cases, additional tests, such as a polysomnogram or multiple sleep latency test, may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Narcolepsy
While there is no cure for narcolepsy, several treatment options can help manage the symptoms and improve overall quality of life. These may include:
1. Medications: Stimulants, such as modafinil or armodafinil, can help promote wakefulness during the day. Antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), may be prescribed to manage cataplexy and other symptoms.
2. Lifestyle Modifications: Establishing a regular sleep schedule, practicing good sleep hygiene, and incorporating planned naps into the daily routine can help manage excessive daytime sleepiness.
3. Supportive Therapies: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and counseling can assist individuals in coping with the emotional and psychological challenges associated with narcolepsy.
In conclusion, narcolepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, cataplexy, sleep paralysis, and hypnagogic hallucinations. Living with narcolepsy can impact various aspects of a person’s life, including work, relationships, and emotional well-being. Seeking proper diagnosis and treatment can help individuals manage the symptoms and improve their overall quality of life.
Key Takeaways: What are the symptoms of narcolepsy?
- Narcolepsy is a sleep disorder that causes excessive daytime sleepiness.
- One common symptom is sudden and uncontrollable sleep attacks.
- People with narcolepsy may experience cataplexy, a sudden loss of muscle tone triggered by emotions.
- Hallucinations, sleep paralysis, and disrupted nighttime sleep are also common symptoms.
- Diagnosis of narcolepsy often involves a sleep study and evaluation of symptoms by a healthcare professional.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of narcolepsy?
Narcolepsy is a sleep disorder that affects the brain’s ability to regulate sleep-wake cycles. The most common symptom of narcolepsy is excessive daytime sleepiness, where individuals experience an overwhelming urge to sleep throughout the day. This can result in sudden and uncontrollable sleep attacks, often at inappropriate times and places.
In addition to excessive sleepiness, narcolepsy can also cause cataplexy, which is the sudden loss of muscle tone and control. This can range from mild weakness to complete paralysis, usually triggered by strong emotions such as laughter or anger. Other symptoms include sleep paralysis, hallucinations, and disrupted nighttime sleep.
Can narcolepsy cause hallucinations?
Yes, narcolepsy can cause hallucinations, particularly during sleep onset or upon awakening. These hallucinations are known as hypnagogic or hypnopompic hallucinations, depending on whether they occur while falling asleep or waking up. They can be vivid and realistic, involving visual, auditory, or tactile sensations.
Hallucinations in narcolepsy are often accompanied by sleep paralysis, a temporary inability to move or speak while transitioning between sleep and wakefulness. These experiences can be frightening or disorienting, but they are generally harmless and last only a few minutes.
What is cataplexy and how does it relate to narcolepsy?
Cataplexy is a characteristic symptom of narcolepsy, where individuals experience sudden episodes of muscle weakness or complete loss of muscle control. These episodes are usually triggered by strong emotions such as laughter, surprise, or anger. Cataplexy can range from mild muscle weakness, causing a slackening of facial muscles, to complete collapse and temporary paralysis.
During a cataplectic episode, individuals remain fully conscious and aware of their surroundings, but they are unable to move or speak until the episode passes. Cataplexy can be disruptive and affect daily activities, but it can be managed through lifestyle changes and medications.
Why do people with narcolepsy experience disrupted nighttime sleep?
People with narcolepsy often experience disrupted nighttime sleep due to a variety of factors. One common factor is the frequent occurrence of vivid dreams and nightmares, which can interrupt sleep and lead to awakenings. Additionally, individuals with narcolepsy may experience sleep fragmentation, where their sleep is divided into multiple shorter periods instead of a consolidated, uninterrupted sleep.
Another reason for disrupted nighttime sleep in narcolepsy is the presence of other sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome, which can coexist with narcolepsy. These disorders can further disrupt sleep and exacerbate daytime sleepiness. It is important for individuals with narcolepsy to address any underlying sleep disorders to improve the quality of their sleep.
What are some lifestyle modifications that can help manage narcolepsy symptoms?
While there is no cure for narcolepsy, certain lifestyle modifications can help manage its symptoms. Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule is crucial, which includes going to bed and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This can help regulate the sleep-wake cycle and reduce excessive daytime sleepiness.
Avoiding stimulants such as caffeine and alcohol close to bedtime is also recommended, as they can disrupt sleep. Regular exercise during the day can promote better sleep at night and help manage narcolepsy symptoms. Creating a sleep-friendly environment, with a comfortable bed, cool temperature, and minimal noise and light, can also improve sleep quality.
Narcolepsy (NORD) – causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, pathology
Final Summary: Understanding the Symptoms of Narcolepsy
After delving into the world of narcolepsy and its symptoms, it’s clear that this sleep disorder is no laughing matter. From excessive daytime sleepiness to sudden muscle weakness, the symptoms of narcolepsy can greatly impact one’s daily life. It’s important to recognize these signs in order to seek proper diagnosis and treatment.
One of the key symptoms of narcolepsy is excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS), which can result in uncontrollable bouts of sleepiness throughout the day. Imagine trying to focus on a task, only to be overcome by an overwhelming urge to sleep. This can be frustrating and even dangerous, especially when driving or operating machinery. Another symptom to watch out for is cataplexy, a sudden loss of muscle tone that can cause weakness or even temporary paralysis. It can be triggered by strong emotions such as laughter or anger, making social situations a potential minefield for those with narcolepsy.
Other symptoms include sleep paralysis, where individuals are temporarily unable to move or speak when falling asleep or waking up, as well as vivid hallucinations that occur during these transitions. These experiences can be incredibly unsettling and may contribute to feelings of anxiety or fear surrounding sleep. Additionally, disrupted nighttime sleep is common in individuals with narcolepsy, leading to a cycle of sleep deprivation that further exacerbates the symptoms.
In conclusion, narcolepsy is a complex sleep disorder with a range of symptoms that can significantly impact a person’s life. By understanding and recognizing these symptoms, individuals can seek appropriate medical help and explore treatment options that can improve their quality of life. Whether it’s medication, behavioral changes, or support from loved ones, managing narcolepsy is possible with the right approach. So, if you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, don’t hesitate to reach out for help and take the first step towards a restful and fulfilling life.