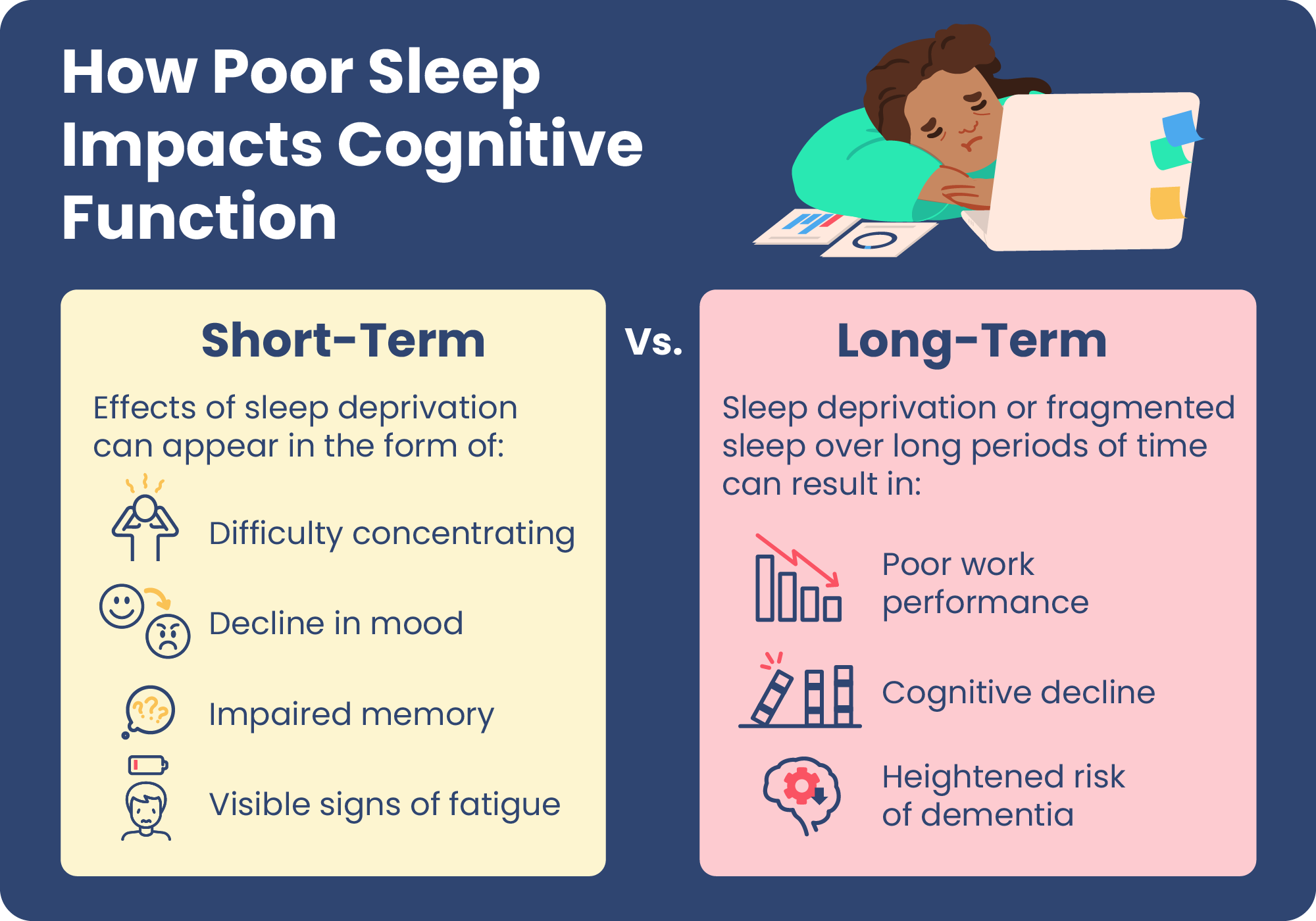
Sleep deprivation is a common issue that many people face in today’s fast-paced world. We all know that getting a good night’s sleep is important for our overall health and well-being, but did you know that it also plays a crucial role in our brain function? In this article, we will dive into the fascinating topic of sleep deprivation and its cognitive consequences. So, grab a cup of coffee and get ready to explore how lack of sleep can affect your brain in ways you never imagined!
When it comes to sleep deprivation, our brains are the first ones to suffer the consequences. Sleep deprivation can have a profound impact on our cognitive abilities, affecting our memory, attention, decision-making skills, and overall mental clarity. It’s like trying to navigate through a foggy maze without a flashlight – you may stumble upon dead ends, forget important details, and struggle to find your way out.
So, what exactly happens to our brains when we don’t get enough sleep? Well, for starters, our brain’s ability to consolidate and retain information becomes compromised. It’s like that old saying, “You snooze, you lose.” Without sufficient sleep, our brains struggle to process and store new information, making it harder for us to recall things later on. Additionally, sleep deprivation can also impair our ability to focus and concentrate, leading to decreased productivity and increased errors in our daily tasks.
Understanding the cognitive consequences of sleep deprivation is crucial for our overall well-being. So, let’s delve deeper into the fascinating world of sleep and discover how we can prioritize restful nights for a sharper and more alert mind. But first, grab a quick power nap if you need to – we wouldn’t want you falling asleep while reading this captivating article!
Sleep Deprivation and Your Brain: Understanding Cognitive Consequences
Sleep deprivation can have significant effects on your brain’s cognitive function. Lack of sleep impairs attention, memory, and decision-making abilities. It can also lead to mood swings, irritability, and decreased productivity. Research shows that chronic sleep deprivation increases the risk of developing neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. It is important to prioritize sleep and establish healthy sleep habits to maintain optimal brain function and overall well-being.
Sleep Deprivation and Your Brain: Understanding Cognitive Consequences
Sleep deprivation is a common issue that affects many individuals in today’s fast-paced society. With busy schedules, demanding workloads, and various other responsibilities, getting a good night’s sleep often takes a backseat. However, the consequences of sleep deprivation on the brain and cognitive function should not be underestimated. In this article, we will explore the impact of sleep deprivation on the brain and discuss the cognitive consequences that can arise from a lack of sleep.
The Importance of Sleep for Brain Health
Sleep plays a vital role in maintaining overall brain health. During sleep, the brain undergoes essential processes that are crucial for memory consolidation, learning, and problem-solving. When we sleep, our brain goes through different stages, including rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep. Each stage has specific functions that contribute to different aspects of cognitive function.
During REM sleep, our brain is highly active, and this is when dreaming occurs. REM sleep is essential for processing emotions and enhancing creativity. On the other hand, NREM sleep is involved in memory consolidation, allowing the brain to strengthen newly acquired information and store it for later retrieval. Without sufficient sleep, these processes can be disrupted, leading to cognitive impairment.
Sleep deprivation can have a significant impact on various cognitive functions, including attention, memory, executive function, and decision-making. Let’s delve deeper into the specific cognitive consequences of sleep deprivation.
Attention and Sleep Deprivation
One of the most noticeable effects of sleep deprivation is the impairment of attention. When we are sleep-deprived, it becomes challenging to stay focused and concentrate on tasks. Our ability to sustain attention for long periods is compromised, leading to decreased productivity and increased errors. Sleep-deprived individuals may find it difficult to pay attention to conversations, complete work assignments, or even drive safely.
Furthermore, sleep deprivation can also affect our ability to shift attention effectively. This means that we may struggle to switch between tasks or adapt to new stimuli, making it difficult to multitask or handle complex situations. The lack of sleep can significantly hinder our overall cognitive performance.
Memory and Sleep Deprivation
Memory is another cognitive function that is greatly influenced by sleep deprivation. When we sleep, the brain consolidates memories, transferring information from short-term memory to long-term memory. This process is crucial for learning and retaining new information. However, when we don’t get enough sleep, this consolidation process is disrupted, leading to difficulties in memory formation and retrieval.
Sleep-deprived individuals may experience problems with both short-term and long-term memory. They may struggle to remember details, recall important information, or even have difficulty learning new things. Sleep deprivation can also affect memory recall, making it challenging to retrieve previously learned information. This can have a significant impact on academic performance, work productivity, and daily functioning.
In addition to impairing attention and memory, sleep deprivation can also have consequences on executive function and decision-making. These cognitive functions are essential for planning, problem-solving, and controlling impulses. When we are sleep-deprived, our ability to think critically and make sound decisions becomes compromised. We may experience difficulties in solving complex problems, exhibit poor judgment, and struggle to regulate our emotions effectively.
Overall, the cognitive consequences of sleep deprivation are far-reaching and can significantly impact our daily lives. From attention and memory to executive function and decision-making, sleep deprivation takes a toll on our brain health. It is crucial to prioritize sleep and establish healthy sleep habits to ensure optimal cognitive function and overall well-being.
The Role of Sleep Hygiene in Brain Health
To mitigate the cognitive consequences of sleep deprivation, it is essential to prioritize sleep hygiene. Sleep hygiene refers to the practices and habits that promote healthy sleep. By adopting good sleep hygiene practices, we can improve the quality and duration of our sleep, leading to better cognitive function and overall brain health.
Here are some tips to improve sleep hygiene:
Establish a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day helps regulate our internal body clock and promotes better sleep. Consistency is key when it comes to sleep, so try to stick to a regular sleep schedule even on weekends.
Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine
Engage in relaxing activities before bed to signal to your body that it’s time to wind down. This can include reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation.
Create a Sleep-Friendly Environment
Ensure that your sleep environment is conducive to quality sleep. Make sure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool. Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows that provide adequate support. Consider using earplugs, eye masks, or white noise machines to block out any distractions.
Avoid Stimulants and Electronics Before Bed
Avoid consuming stimulants such as caffeine or nicotine close to bedtime, as they can interfere with sleep. Additionally, limit your exposure to electronic devices, as the blue light emitted by screens can disrupt the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep.
Create a Relaxing Bedtime Ritual
Engage in relaxing activities before bed to signal to your body that it’s time to wind down. This can include reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation.
By implementing these sleep hygiene practices, you can improve the quality and duration of your sleep, ultimately enhancing your brain health and cognitive function.
Benefits of Prioritizing Sleep
Prioritizing sleep has numerous benefits beyond cognitive function. Getting enough sleep on a regular basis can:
– Improve mood and emotional well-being
– Boost immune function
– Enhance physical performance and recovery
– Lower the risk of chronic health conditions such as heart disease and diabetes
– Aid in weight management
– Improve overall quality of life
By recognizing the importance of sleep and making it a priority in your daily routine, you can reap these benefits and optimize your overall health and well-being.
Sleep Deprivation vs. Optimal Sleep: The Impact on Cognitive Function
To further understand the cognitive consequences of sleep deprivation, let’s compare the effects of sleep deprivation with optimal sleep on various cognitive functions.
Attention
Sleep Deprivation: Sleep deprivation impairs attention, making it difficult to focus and sustain attention for extended periods. Sleep-deprived individuals may experience increased distractibility and reduced ability to switch attention between tasks.
Optimal Sleep: Adequate sleep enhances attention, allowing individuals to stay focused and concentrate on tasks. Optimal sleep promotes sustained attention and facilitates task switching and adaptability.
Memory
Sleep Deprivation: Lack of sleep disrupts the memory consolidation process, leading to difficulties in forming and retrieving memories. Sleep-deprived individuals may experience problems with both short-term and long-term memory.
Optimal Sleep: Sufficient sleep facilitates memory consolidation, promoting effective learning and memory formation. Optimal sleep enhances memory recall and the retention of learned information.
Executive Function
Sleep Deprivation: Sleep deprivation impairs executive function, making it difficult to plan, problem-solve, and control impulses. Sleep-deprived individuals may exhibit poor judgment and struggle to regulate their emotions effectively.
Optimal Sleep: Adequate sleep supports optimal executive function, enhancing critical thinking, problem-solving abilities, and emotional regulation. Optimal sleep promotes sound decision-making and effective impulse control.
Mood and Emotional Well-being
Sleep Deprivation: Lack of sleep can lead to mood disturbances, irritability, and increased emotional reactivity. Sleep-deprived individuals may experience elevated levels of stress, anxiety, and depression.
Optimal Sleep: Sufficient sleep promotes emotional well-being, stability, and resilience. Optimal sleep contributes to a positive mood, reduced stress levels, and improved overall emotional health.
By comparing the effects of sleep deprivation and optimal sleep on cognitive function, it becomes evident that prioritizing sleep is crucial for maintaining optimal brain health and cognitive performance.
Tips for Better Sleep
To improve the quality and duration of your sleep, consider implementing the following tips:
– Create a relaxing bedtime routine to signal to your body that it’s time to sleep
– Establish a consistent sleep schedule, going to bed and waking up at the same time each day
– Ensure your sleep environment is comfortable, quiet, and dark
– Avoid stimulants such as caffeine and nicotine close to bedtime
– Limit your exposure to electronic devices before bed
– Engage in regular physical activity, but avoid exercising too close to bedtime
– Manage stress through relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or meditation
– Avoid heavy meals and excessive fluid intake close to bedtime
– Consider incorporating natural sleep aids such as herbal teas or essential oils
By implementing these tips, you can improve your sleep quality and promote optimal brain health and cognitive function.
Conclusion
Sleep deprivation has significant cognitive consequences, affecting attention, memory, executive function, and emotional well-being. Prioritizing sleep and adopting healthy sleep habits are essential for maintaining optimal brain health and cognitive performance. By understanding the impact of sleep deprivation on the brain, we can make informed choices to ensure we get the sleep we need to thrive. Remember, a good night’s sleep is not a luxury but a necessity for overall well-being.
Key Takeaways: Sleep Deprivation and Your Brain: Understanding Cognitive Consequences
- Lack of sleep can negatively affect your memory and ability to concentrate.
- Sleep deprivation can lead to increased mood swings and irritability.
- Insufficient sleep can impair decision-making and problem-solving skills.
- Chronic sleep deprivation may increase the risk of developing mental health disorders.
- Adequate sleep is essential for optimal brain function and overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the cognitive consequences of sleep deprivation?
Sleep deprivation can have significant cognitive consequences on the brain. When you don’t get enough sleep, your brain’s ability to function optimally is compromised. One of the most noticeable consequences is a decline in attention and concentration. Sleep-deprived individuals often struggle to stay focused, have difficulty processing information, and may experience frequent lapses in memory.
Additionally, sleep deprivation can negatively impact decision-making skills. Studies have shown that sleep-deprived individuals tend to make riskier decisions and have difficulty evaluating the potential consequences of their actions. This can have serious implications in various aspects of life, from work performance to personal relationships.
How does sleep deprivation affect learning and memory?
Sleep plays a crucial role in learning and memory consolidation. When you sleep, your brain processes and stores information from the day, helping to solidify memories. However, when you are sleep deprived, this process is disrupted.
Research has shown that lack of sleep impairs both short-term and long-term memory. Sleep-deprived individuals may struggle to retain new information and have difficulty recalling previously learned material. This can have a significant impact on academic performance and overall cognitive functioning.
Can sleep deprivation lead to mood disorders?
Yes, sleep deprivation can contribute to the development of mood disorders. Chronic sleep deprivation disrupts the delicate balance of chemicals in the brain that regulate mood, such as serotonin and dopamine. This imbalance can lead to increased irritability, mood swings, and even depression.
Furthermore, the lack of quality sleep can exacerbate existing mood disorders. It can make symptoms more severe and make it more challenging to manage emotions effectively. Getting enough sleep is essential for maintaining optimal mental health and emotional well-being.
Does sleep deprivation impact cognitive performance in the long term?
Yes, long-term sleep deprivation can have lasting effects on cognitive performance. Prolonged sleep deprivation can lead to cognitive decline, affecting various cognitive functions such as attention, memory, and problem-solving abilities.
Studies have shown that chronic sleep deprivation is associated with an increased risk of developing neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease. Sleep is crucial for brain health and allowing the brain to repair and rejuvenate itself. Continually depriving the brain of adequate rest can have detrimental effects on cognitive function in the long run.
What are some strategies to improve sleep and prevent cognitive consequences?
There are several strategies you can implement to improve sleep and mitigate the cognitive consequences of sleep deprivation. One of the most important is establishing a consistent sleep routine. Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps regulate your body’s internal clock.
Avoiding stimulants such as caffeine and electronic devices before bedtime can also promote better sleep. Creating a relaxing bedtime routine, such as reading or practicing relaxation techniques, can signal to your body that it’s time to wind down.
Creating a sleep-friendly environment, with a comfortable mattress and a cool, dark, and quiet bedroom, can also help improve sleep quality. If sleep problems persist, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to identify and address any underlying sleep disorders.
Sleep deprivation and memory problems | Robbert Havekes | TEDxDenHelder
Final Thoughts: The Impact of Sleep Deprivation on Your Brain
After exploring the topic of sleep deprivation and its cognitive consequences, it is clear that getting enough quality sleep is crucial for optimal brain function. Sleep deprivation can have detrimental effects on various aspects of cognitive function, including attention, memory, decision-making, and creativity. It impairs our ability to focus, process information, and make sound judgments.
The research shows that sleep deprivation affects the brain at a fundamental level, disrupting neural pathways and impairing communication between different regions of the brain. This can lead to decreased cognitive performance, increased risk of accidents, and even long-term cognitive decline. It is essential to prioritize sleep and establish healthy sleep habits to protect our brain health and overall well-being.
Remember, a good night’s sleep is not a luxury but a necessity. By ensuring we prioritize sleep and create a conducive sleep environment, we can enhance our cognitive function, improve our productivity, and promote our overall mental and physical health. So, let’s prioritize our sleep and give our brains the rest they deserve for a sharper, brighter tomorrow.