Have you ever wondered how sleepwalking is diagnosed? It’s a fascinating topic that sheds light on the mysterious world of sleep disorders. Whether you’re a curious individual or someone who suspects they might be sleepwalking, understanding the diagnostic process can provide valuable insights. So, let’s dive in and explore how professionals identify and diagnose sleepwalking.
When it comes to diagnosing sleepwalking, healthcare providers rely on a combination of factors. They start by gathering information about the individual’s sleep patterns, behaviors, and any related symptoms. This may involve asking questions about the frequency and duration of sleepwalking episodes, as well as any potential triggers. Additionally, a thorough medical history review is conducted to identify any underlying health conditions or medications that could contribute to sleepwalking. With all this information in hand, healthcare providers can then make an accurate diagnosis and offer appropriate treatment options. So, let’s unravel the mystery of sleepwalking diagnosis together!
How is Sleepwalking Diagnosed?
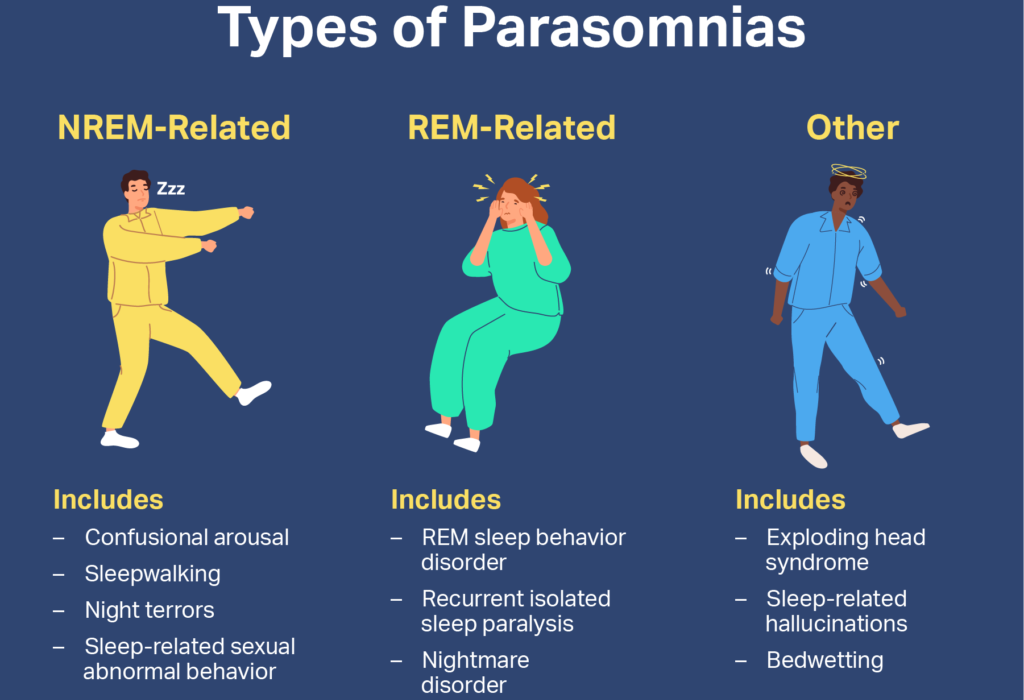
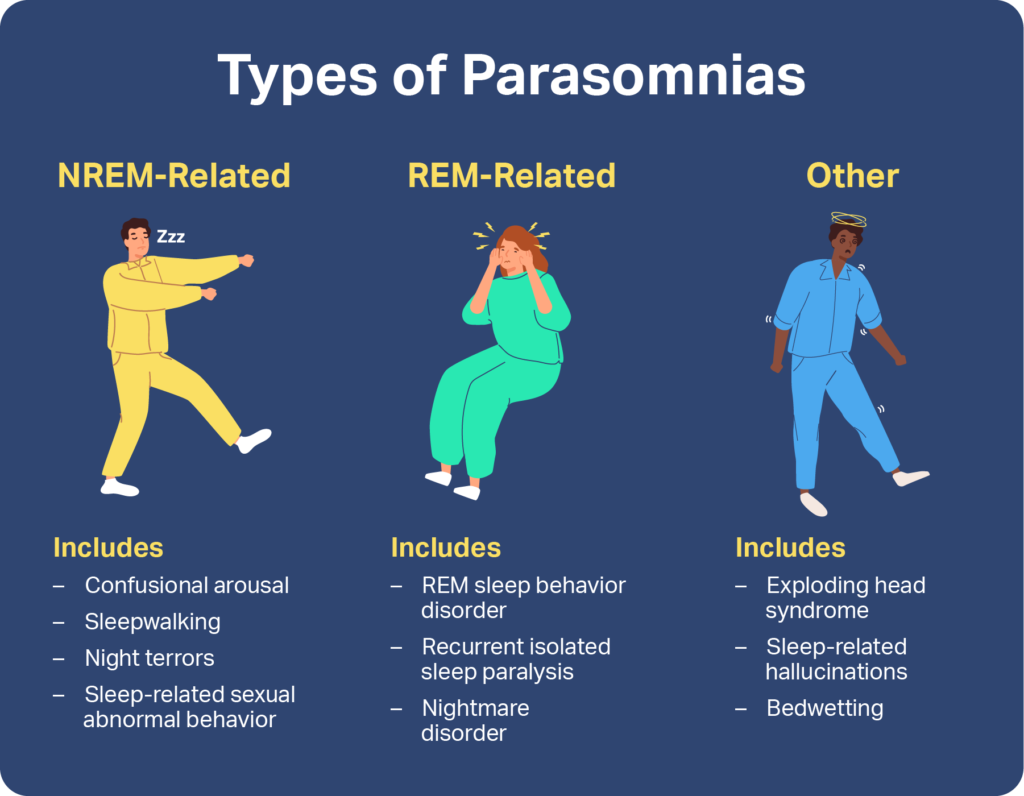
Sleepwalking, also known as somnambulism, is a sleep disorder that involves performing complex actions while still asleep. It can be a perplexing and potentially dangerous condition, but fortunately, it can be diagnosed through a variety of methods. In this article, we will explore the various ways in which sleepwalking is diagnosed and the steps that can be taken to identify and manage this sleep disorder.
Medical History and Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing sleepwalking is a thorough medical history and physical examination. A healthcare professional will gather information about the individual’s sleep patterns, any previous sleepwalking episodes, and any other sleep-related issues. They will also inquire about the individual’s overall health, medications, and lifestyle factors that may contribute to sleepwalking.
During the physical examination, the healthcare professional will look for any underlying medical conditions or physical factors that may be contributing to sleepwalking. They may also assess the individual’s sleep hygiene, which includes factors such as the sleep environment, bedtime routine, and overall sleep quality. By gathering this information, the healthcare professional can gain valuable insights into the potential causes and triggers of sleepwalking.
Sleep Diary
A sleep diary is a useful tool in diagnosing sleep disorders, including sleepwalking. The individual is asked to record their sleep patterns and any sleepwalking episodes over a period of time, usually for at least two weeks. The sleep diary may include information such as the time the individual goes to bed, the time they wake up, and any disturbances or events that occur during the night.
By analyzing the sleep diary, healthcare professionals can identify patterns and trends in the individual’s sleepwalking episodes. They can determine the frequency, duration, and timing of the sleepwalking episodes, as well as any potential triggers or factors that may be contributing to the condition. This information can guide further diagnostic tests and treatment plans.
Nocturnal Polysomnography
Nocturnal polysomnography is a comprehensive sleep study that is often used to diagnose sleep disorders, including sleepwalking. The individual is monitored overnight in a sleep laboratory, where various physiological parameters are recorded. These parameters may include brain activity (EEG), eye movements (EOG), muscle activity (EMG), heart rate, and breathing patterns.
During the sleep study, the healthcare professionals can observe and analyze the individual’s sleep stages and identify any abnormal behaviors, such as sleepwalking. They can also assess the overall quality of sleep, the presence of other sleep disorders, and any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to sleepwalking.
Multiple Sleep Latency Test
In some cases, a multiple sleep latency test (MSLT) may be conducted to assess daytime sleepiness and the individual’s ability to fall asleep during the day. This test involves a series of naps scheduled at specific intervals throughout the day. The individual is monitored to determine how quickly they fall asleep during these naps and whether they enter rapid eye movement (REM) sleep.
The MSLT can provide valuable information about the individual’s sleep-wake patterns and any excessive daytime sleepiness that may be associated with sleepwalking. It can also help differentiate sleepwalking from other sleep disorders, such as narcolepsy.
Video Monitoring
Video monitoring is another diagnostic tool that can be used to observe and document sleepwalking episodes. The individual may be asked to set up a video camera in their bedroom to capture any sleepwalking behaviors. This visual evidence can provide valuable insights into the nature and severity of the sleepwalking episodes, as well as any potential safety concerns.
By reviewing the video recordings, healthcare professionals can confirm the diagnosis of sleepwalking and gain a better understanding of the individual’s sleepwalking patterns. This information can guide the development of a personalized treatment plan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, sleepwalking can be diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, sleep diary, nocturnal polysomnography, multiple sleep latency test, and video monitoring. These diagnostic methods help healthcare professionals understand the nature and triggers of sleepwalking episodes, enabling them to develop an effective treatment plan. If you or someone you know experiences sleepwalking, it is important to seek medical attention to ensure proper diagnosis and management of this sleep disorder.
Key Takeaways: How is sleepwalking diagnosed?
- Sleepwalking is diagnosed through a careful evaluation of symptoms and medical history.
- Doctors may ask about sleep patterns, sleep environment, and any related episodes.
- Observing the person’s behavior during sleep can help in diagnosis.
- In some cases, sleep studies may be conducted to monitor brain activity during sleep.
- It is important to rule out any underlying medical conditions or medications that may contribute to sleepwalking.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the common symptoms of sleepwalking?
Sleepwalking, also known as somnambulism, is a sleep disorder characterized by complex movements and behaviors during sleep. Common symptoms of sleepwalking include getting out of bed and walking around, performing routine activities, talking or mumbling, and having a glassy-eyed or blank expression. Sleepwalkers may also have difficulty waking up during an episode and may not remember the sleepwalking episode upon awakening.
It is important to note that sleepwalking can vary in severity and frequency from person to person. While some individuals may only experience occasional episodes, others may sleepwalk regularly, sometimes even multiple times a night.
What causes sleepwalking?
The exact cause of sleepwalking is not fully understood, but several factors can contribute to its occurrence. Sleep deprivation, irregular sleep schedules, stress and anxiety, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions such as sleep apnea or restless leg syndrome have been associated with an increased risk of sleepwalking.
Additionally, sleepwalking tends to run in families, suggesting a genetic component. Certain lifestyle factors, such as excessive alcohol consumption or drug use, can also trigger sleepwalking episodes in susceptible individuals.
How is sleepwalking diagnosed?
Sleepwalking is typically diagnosed based on a thorough evaluation of the individual’s medical history and sleep behaviors. A healthcare professional, such as a sleep specialist, may conduct a comprehensive assessment, which may include:
1. Detailed interview: The healthcare professional will ask about the frequency, duration, and characteristics of the sleepwalking episodes. They may also inquire about any potential triggers or underlying medical conditions.
2. Sleep diary: Keeping a sleep diary can help track sleep patterns, including the occurrence of sleepwalking episodes. This can provide valuable information for diagnosis and treatment planning.
3. Overnight sleep study: In some cases, a polysomnography may be recommended to monitor brain activity, breathing patterns, and movements during sleep. This can help rule out other sleep disorders and confirm the diagnosis of sleepwalking.
Can sleepwalking be treated?
Yes, sleepwalking can be managed and treated. Treatment options may vary depending on the underlying causes and severity of the sleepwalking episodes. Some suggested strategies include:
1. Improving sleep hygiene: Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensuring a comfortable sleep environment can help reduce the likelihood of sleepwalking.
2. Addressing underlying medical conditions: If sleep apnea, restless leg syndrome, or other medical conditions are contributing to sleepwalking, treating these conditions may help alleviate symptoms.
3. Medication: In certain cases, a healthcare professional may prescribe medications such as benzodiazepines or antidepressants to help regulate sleep patterns and reduce sleepwalking episodes.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Are there any safety measures for sleepwalkers?
Ensuring the safety of sleepwalkers is crucial to prevent any potential injuries during episodes. Consider implementing the following safety measures:
1. Clear the sleep environment: Remove any objects or obstacles that could cause harm or tripping hazards during sleepwalking episodes.
2. Secure windows and doors: Install locks or alarms on windows and doors to prevent sleepwalkers from wandering outside or accessing potentially dangerous areas.
3. Use safety gates or barriers: If sleepwalkers are prone to leaving their bedroom, using safety gates or barriers can help confine them to a safe area.
4. Notify household members: Inform family members or roommates about the sleepwalker’s condition to ensure they are aware and can assist if necessary.
5. Seek professional guidance: Consulting with a healthcare professional or sleep specialist can provide additional guidance and specific safety recommendations based on the individual’s sleepwalking patterns.
How Does Sleepwalking Work?
Final Summary: How is Sleepwalking Diagnosed?
When it comes to diagnosing sleepwalking, medical professionals employ a variety of methods to determine whether someone is experiencing this peculiar sleep disorder. While there isn’t a specific test that can definitively diagnose sleepwalking, doctors rely on a combination of physical exams, sleep studies, and a thorough analysis of the individual’s medical history and sleep patterns.
During a physical examination, doctors check for any underlying medical conditions that could be contributing to sleepwalking episodes. They may also inquire about the individual’s sleep habits, such as the frequency and duration of episodes, any triggering factors, and whether there are any associated injuries. This information can help paint a clearer picture of the individual’s sleepwalking patterns and aid in the diagnosis.
In addition to the physical examination, sleep studies play a crucial role in diagnosing sleepwalking. These studies, known as polysomnography, involve monitoring brain activity, heart rate, breathing patterns, and muscle movements during sleep. By observing these physiological markers, sleep specialists can identify abnormal sleep behaviors, including sleepwalking, and differentiate them from other sleep disorders.
To further validate the diagnosis, medical professionals also take into account the individual’s medical history. They inquire about any family history of sleepwalking or other sleep disorders, as there may be a genetic component involved. Additionally, they look for any signs of stress, anxiety, or medication use that may be contributing to the sleepwalking episodes.
In conclusion, diagnosing sleepwalking requires a comprehensive approach that combines physical examinations, sleep studies, and an analysis of the individual’s medical history. By considering these various factors, doctors can accurately identify and understand the unique sleepwalking patterns exhibited by each individual. So, if you or someone you know experiences sleepwalking, seeking medical advice and undergoing the necessary evaluations can provide valuable insights and help manage this intriguing sleep disorder.