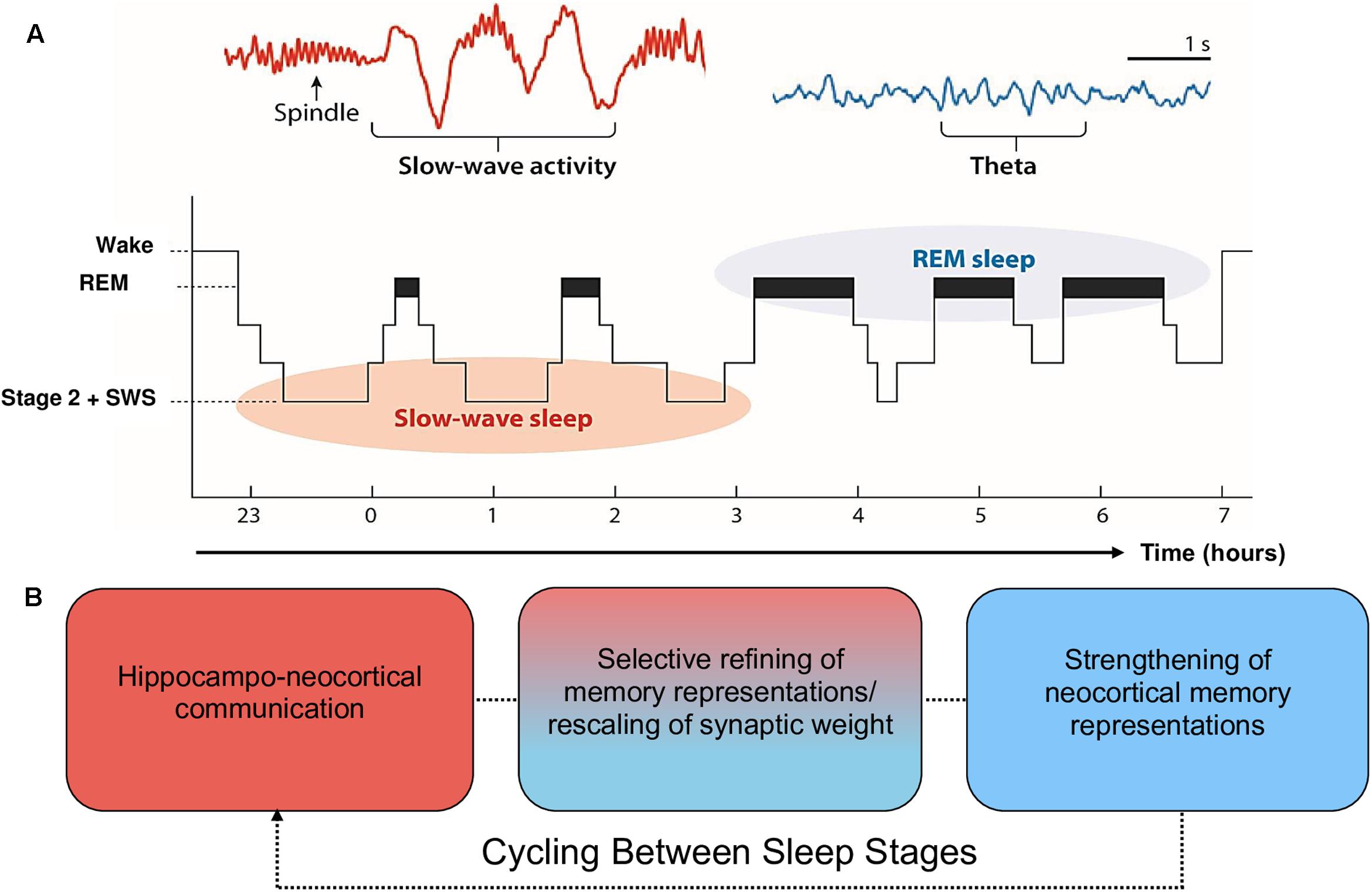
Did you know that even light sleep can play a significant role in memory consolidation and learning? It may seem counterintuitive, as we often associate deep, uninterrupted sleep with these cognitive processes. However, research has shown that light sleep, characterized by rapid eye movement (REM) sleep and stage 2 non-REM sleep, actually contributes to the formation and retention of memories. So, if you’ve ever wondered why you sometimes wake up feeling like you’ve learned something new overnight, light sleep might just be the answer!
During light sleep, our brains are still active, even though our bodies may not be as deeply relaxed as during deep sleep. This is when our brains go through cycles of REM sleep, where dreams occur, and stage 2 non-REM sleep, which is a lighter form of sleep. These cycles are crucial for memory consolidation and learning. During REM sleep, the brain processes and consolidates emotional and procedural memories, while stage 2 non-REM sleep plays a role in consolidating declarative memories, such as facts and events. So, even though we may not be in a state of deep slumber, our brains are hard at work, solidifying the knowledge and experiences we’ve acquired throughout the day.
In conclusion, light sleep should not be underestimated when it comes to memory consolidation and learning. While deep sleep is undoubtedly important for overall rest and rejuvenation, light sleep plays a unique role in the cognitive processes that shape our memories. So, the next time you find yourself drifting in and out of dreams during the night, remember that your brain is busy laying down the foundations of new knowledge. Embrace the power of light sleep and let it contribute to your journey of continuous learning and memory formation.
Does Light Sleep Contribute to Memory Consolidation and Learning?
Light sleep, also known as non-REM stage 1 sleep, is a crucial part of the sleep cycle. While deep sleep and REM sleep are well-known for their roles in memory consolidation and learning, the contribution of light sleep to these cognitive processes is often overlooked. In this article, we will explore the impact of light sleep on memory and learning and shed light on its importance in optimizing brain function.
The Role of Light Sleep in Memory Consolidation
Light sleep is the transitional phase between wakefulness and deep sleep. During this stage, brain activity slows down, and the body relaxes. Contrary to popular belief, light sleep is not a useless or unimportant part of the sleep cycle. In fact, research suggests that it plays a crucial role in memory consolidation.
One of the primary functions of light sleep is to filter and process information gathered during wakefulness. As we go about our day, our brains are bombarded with a constant stream of sensory input. Light sleep allows the brain to sort through this information, discard irrelevant details, and extract the essential elements that contribute to memory formation. Without this filtering process, our memories would be overwhelmed with unnecessary information, making it difficult to retrieve and utilize them effectively.
Enhancing Learning During Light Sleep
Not only does light sleep contribute to memory consolidation, but it also enhances learning. Research has shown that during light sleep, the brain actively strengthens the connections between newly acquired information and existing knowledge. This process, known as synaptic plasticity, plays a vital role in the formation of long-term memories and the integration of new information into our existing knowledge networks.
During light sleep, the brain also consolidates procedural memories, which are memories related to skills and tasks. This consolidation process allows us to perform these tasks more efficiently and effectively in the future. Therefore, if you’re learning a new skill or studying complex information, getting enough light sleep is essential for maximizing your learning potential.
Overall, light sleep is not a passive or insignificant stage of sleep. It actively contributes to memory consolidation and learning processes, allowing us to retain and utilize information more effectively.
The Effects of Light Sleep Deprivation on Memory and Learning
While light sleep is crucial for memory and learning, the consequences of light sleep deprivation can be detrimental to cognitive function. When we don’t get enough light sleep, our ability to consolidate memories and learn new information is compromised.
Studies have shown that sleep deprivation, especially the deprivation of light sleep, can lead to impaired memory performance. Without sufficient light sleep, the brain struggles to filter and process information effectively, resulting in difficulties in memory retrieval and retention. This can negatively impact academic performance, work productivity, and overall cognitive functioning.
Tips for Optimizing Light Sleep
To ensure you get enough light sleep and optimize its benefits for memory consolidation and learning, consider implementing the following tips:
- Create a sleep-friendly environment: Make sure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and at a comfortable temperature to promote uninterrupted light sleep.
- Establish a consistent sleep schedule: Going to bed and waking up at the same time every day helps regulate your sleep-wake cycle and promotes healthy light sleep.
- Avoid stimulating activities before bed: Engaging in stimulating activities, such as using electronic devices or consuming caffeine, can disrupt your ability to transition into light sleep. Establish a relaxing bedtime routine to prepare your mind and body for sleep.
- Practice good sleep hygiene: Maintain a regular exercise routine, limit daytime napping, and avoid heavy meals close to bedtime to optimize the quality of your light sleep.
- Consider sleep aids: If you’re struggling to get enough light sleep, consult with a healthcare professional to explore potential sleep aids or relaxation techniques that can support your sleep quality.
By prioritizing light sleep and implementing these strategies, you can enhance memory consolidation and learning, leading to improved cognitive performance and overall well-being.
Additional Benefits of Light Sleep
While memory consolidation and learning are key benefits of light sleep, this sleep stage offers additional advantages for our physical and mental health:
- Restoration of energy: Light sleep helps replenish energy levels, leaving us feeling refreshed and rejuvenated upon waking.
- Regulation of emotions: Adequate light sleep is essential for emotional regulation, reducing the risk of mood disorders such as depression and anxiety.
- Enhancement of creativity: Studies have shown that light sleep can boost creative thinking and problem-solving abilities.
- Support for immune function: Light sleep plays a role in strengthening the immune system, promoting overall health and well-being.
- Regulation of appetite and metabolism: Sufficient light sleep helps regulate hunger hormones, contributing to healthy eating habits and weight management.
Given these additional benefits, it is clear that light sleep is not only important for memory consolidation and learning but also for various aspects of our physical and mental health.
Conclusion
Light sleep is a critical stage of the sleep cycle that often goes unnoticed. It is during this stage that our brains filter and process information, consolidate memories, and enhance learning. Light sleep plays a crucial role in memory consolidation, optimizing brain function, and promoting overall well-being. By understanding the importance of light sleep and implementing strategies to support its quality, we can reap the benefits of improved memory, enhanced learning, and a healthier mind and body.
Key Takeaways: Does light sleep contribute to memory consolidation and learning?
- During light sleep, the brain strengthens newly acquired information, which aids in memory consolidation and learning.
- Light sleep plays a crucial role in processing and organizing memories, making them easier to retrieve later.
- Getting enough quality sleep, including light sleep, is essential for optimal cognitive function and memory retention.
- Interrupted or insufficient light sleep can negatively impact memory consolidation and learning abilities.
- Creating a conducive sleep environment and practicing good sleep hygiene can help promote efficient light sleep and enhance memory consolidation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Light sleep plays a crucial role in memory consolidation and learning. During this stage of sleep, the brain processes and organizes information gathered throughout the day, strengthening neural connections and enhancing memory retention. In this article, we will explore the impact of light sleep on memory and learning.
1. How does light sleep contribute to memory consolidation?
During light sleep, the brain transitions between wakefulness and deep sleep. This stage is essential for memory consolidation as it allows the brain to transfer information from short-term to long-term memory. As you enter light sleep, the hippocampus, a region of the brain involved in memory formation, replays and strengthens the neural connections associated with newly acquired knowledge. This process helps solidify memories and make them more accessible in the future.
Additionally, studies have shown that light sleep promotes the production of certain neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine, which play a crucial role in memory consolidation. These neurotransmitters facilitate the communication between neurons, aiding in the storage and retrieval of information.
2. Can light sleep improve learning abilities?
Adequate light sleep is essential for optimal learning abilities. Research has demonstrated that individuals who experience sufficient light sleep are better able to acquire new information and perform cognitive tasks effectively. During light sleep, the brain processes and organizes the information gained during wakefulness, enhancing the ability to retain and recall knowledge.
Furthermore, light sleep is believed to facilitate synaptic plasticity, which is the brain’s ability to adapt and form new connections between neurons. This plasticity is crucial for learning, as it allows the brain to reorganize and strengthen neural networks associated with new skills and information.
3. How can one improve light sleep for better memory consolidation?
There are several strategies that can help improve light sleep and enhance memory consolidation. Firstly, establishing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a relaxing bedtime routine can signal the body and mind that it is time to transition into sleep. This can be achieved by engaging in calming activities such as reading a book, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation.
Avoiding stimulants, such as caffeine and electronic devices, close to bedtime can also promote better light sleep. These substances and activities can interfere with the natural sleep-wake cycle and inhibit the brain’s ability to enter the necessary stages of sleep for memory consolidation. Creating a sleep-friendly environment, with a comfortable mattress, low lighting, and a cool temperature, can also contribute to better light sleep and improved memory consolidation.
4. Are there any negative effects of insufficient light sleep on memory and learning?
Insufficient light sleep can have detrimental effects on memory and learning. When the brain does not receive enough time in light sleep, it may struggle to consolidate and store information effectively. This can lead to difficulties in retaining newly acquired knowledge and recalling it when needed.
Furthermore, inadequate light sleep has been associated with decreased cognitive performance, including impaired attention, problem-solving abilities, and creativity. It can also increase the risk of memory disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease, as uninterrupted light sleep is essential for the brain to clear out toxins and promote overall brain health.
5. Can napping during the day improve memory consolidation and learning?
Napping during the day can indeed improve memory consolidation and learning. Research has shown that short daytime naps, particularly those that include a period of light sleep, can enhance cognitive function and memory performance. These naps provide an opportunity for the brain to process and organize information, similar to the role of light sleep during nighttime sleep.
However, it is important to note that the duration and timing of the nap can impact its effectiveness. Napping for too long or too close to bedtime may interfere with nighttime sleep and disrupt the natural sleep-wake cycle. Therefore, it is recommended to keep daytime naps short (around 20-30 minutes) and avoid napping too late in the day to reap the benefits of improved memory consolidation and learning.
Webinar: The role of sleep in learning and memory consolidation
Final Thought: The Power of Light Sleep in Enhancing Memory and Learning
After delving into the fascinating topic of whether light sleep contributes to memory consolidation and learning, it is evident that there is a strong correlation between the two. While deep sleep is crucial for physical restoration, it is during the lighter stages of sleep that our brains solidify memories and reinforce what we’ve learned. This process, known as memory consolidation, plays a vital role in our ability to retain information and acquire new skills.
During light sleep, our brains engage in a dance of activity and rest, allowing for the optimal conditions for memory consolidation. Research has shown that specific brainwaves, such as theta and sleep spindles, are more prevalent during light sleep and are closely associated with memory formation. These brainwaves help to connect new information with existing knowledge, creating a strong foundation for learning and comprehension.
Furthermore, studies have highlighted the importance of uninterrupted sleep cycles, as disruptions can hinder the memory consolidation process. It is essential to prioritize quality sleep and create a sleep-friendly environment to maximize the benefits of light sleep. By ensuring a consistent sleep schedule, minimizing external disturbances, and practicing relaxation techniques, we can optimize our sleep cycles and enhance our memory and learning capabilities.
In conclusion, light sleep is not to be underestimated when it comes to memory consolidation and learning. Embracing the power of quality sleep, particularly during the lighter stages, can significantly impact our cognitive abilities. So, let’s prioritize our sleep and allow our brains to work their magic, solidifying memories and facilitating our ongoing quest for knowledge. Sleep well, learn well, and unlock the potential of your incredible mind.