Do you ever experience an overwhelming urge to move your legs, especially when you’re trying to relax or sleep? If so, you may be familiar with restless leg syndrome (RLS). But here’s an interesting question: can RLS be a symptom of another underlying medical condition? Let’s dive into this topic and uncover the connections between RLS and other health issues.
Restless leg syndrome, also known as Willis-Ekbom disease, is a neurological disorder characterized by an irresistible urge to move the legs, accompanied by uncomfortable sensations. It’s often described as a crawling, tingling, or burning sensation deep within the legs. While RLS can occur on its own, recent research suggests that it can also be a symptom of other underlying medical conditions.
One condition that has been linked to RLS is iron deficiency anemia. Iron plays a crucial role in producing dopamine, a neurotransmitter that regulates movement. When the body lacks sufficient iron, dopamine levels can be affected, leading to RLS symptoms. Additionally, certain chronic conditions like kidney disease, diabetes, and peripheral neuropathy have also been associated with RLS. The exact mechanisms behind these connections are still being explored, but it’s clear that RLS can sometimes serve as a red flag for other health issues. So, if you’re experiencing the symptoms of RLS, it’s important to consider the possibility of an underlying medical condition and seek appropriate medical attention.
Can RLS be a Symptom of Another Underlying Medical Condition?
Restless Leg Syndrome (RLS) is a neurological disorder characterized by an irresistible urge to move the legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations. While RLS is a primary condition on its own, research suggests that it can sometimes be a symptom of an underlying medical condition. In this article, we will explore the connection between RLS and other health conditions, shedding light on possible causes and treatment options.
Understanding Restless Leg Syndrome
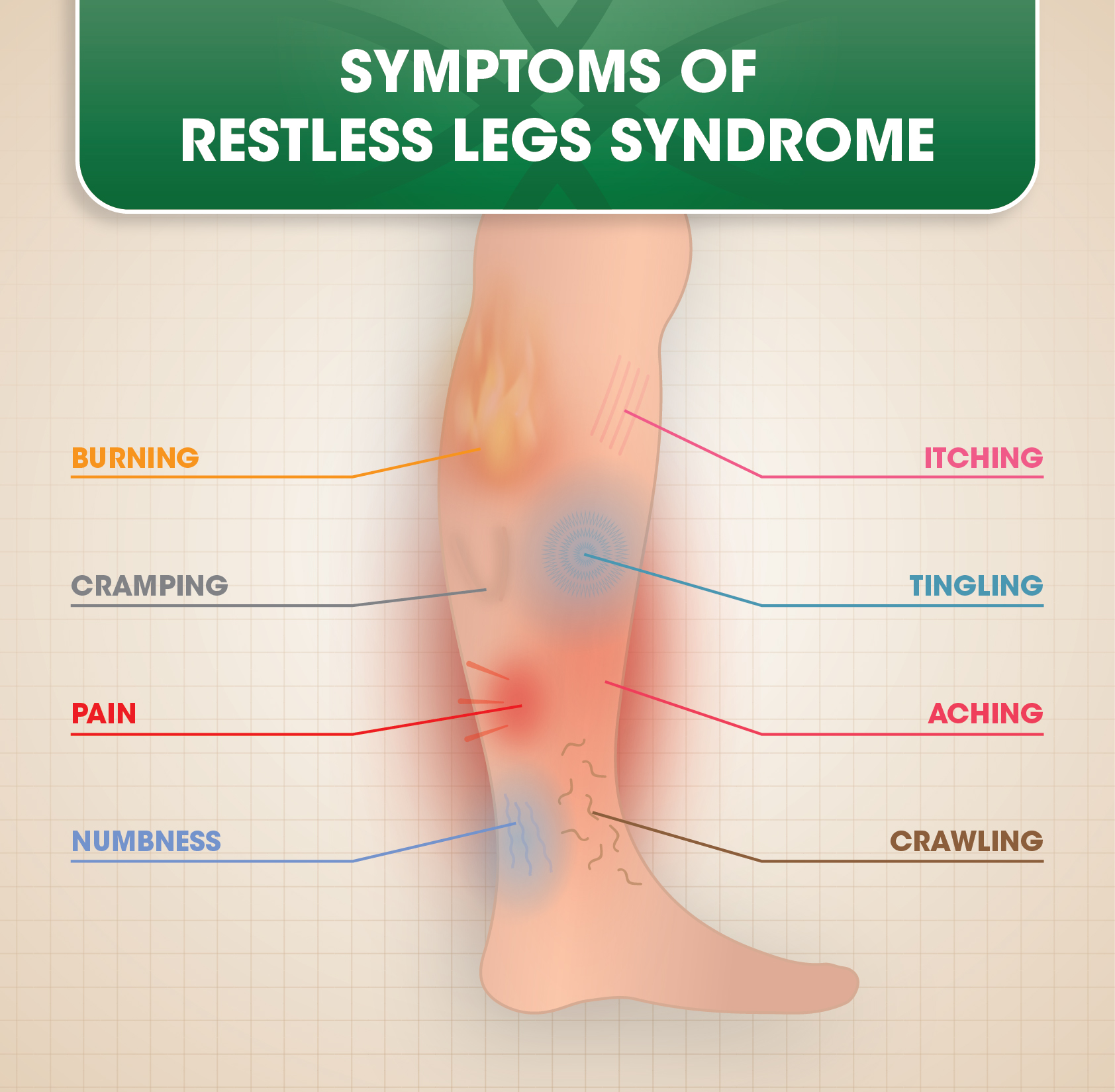
RLS is a condition that affects both the quality of sleep and daily activities of individuals. The symptoms are typically worse in the evening or at night, leading to difficulties falling asleep and staying asleep. People with RLS often describe the sensations in their legs as aching, crawling, tingling, or burning, which are temporarily relieved by movement. The exact cause of RLS is still unknown, but evidence suggests that it may be related to dopamine dysfunction in the brain.
RLS as a Symptom of Iron Deficiency Anemia
Iron deficiency anemia is a common condition that occurs when the body lacks sufficient iron to produce adequate amounts of red blood cells. Research has shown a strong association between RLS and iron deficiency anemia, with studies suggesting that up to 25% of individuals with RLS also have low iron levels. Iron plays a crucial role in the production of dopamine, a neurotransmitter involved in regulating muscle movements. When iron levels are low, dopamine production may be disrupted, leading to the development of RLS symptoms.
Iron supplementation is often recommended as a treatment for RLS associated with iron deficiency anemia. By replenishing iron stores in the body, the symptoms of RLS can be alleviated. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any iron supplements, as excessive iron levels can be harmful.
RLS as a Symptom of Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy refers to damage or dysfunction of the peripheral nerves, which can cause a variety of symptoms, including pain, numbness, and tingling sensations. Some individuals with peripheral neuropathy also experience RLS symptoms. The connection between RLS and peripheral neuropathy is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to disruptions in the sensory pathways that transmit signals between the legs and the brain.
Managing peripheral neuropathy can help alleviate RLS symptoms. Treatments may include medications to manage pain and inflammation, physical therapy to improve muscle strength and coordination, and lifestyle modifications to promote overall well-being.
Other Underlying Medical Conditions Associated with RLS
In addition to iron deficiency anemia and peripheral neuropathy, RLS has been linked to several other medical conditions. These include:
– Kidney disease: Individuals with kidney disease are more likely to develop RLS. The exact mechanisms behind this association are not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to imbalances in electrolytes and fluid retention.
– Diabetes: Research suggests that individuals with diabetes have an increased risk of developing RLS. The underlying cause of this association is still unclear, but it may be related to nerve damage and circulation issues associated with diabetes.
– Pregnancy: RLS is a common symptom experienced by pregnant women, particularly during the third trimester. Hormonal changes, increased blood volume, and pressure on the legs from the growing fetus are believed to contribute to the development of RLS during pregnancy.
– Parkinson’s disease: RLS is more prevalent among individuals with Parkinson’s disease. Both conditions are thought to involve dysfunction in dopamine pathways in the brain.
Managing RLS as a Symptom
When RLS is a symptom of an underlying medical condition, treating the root cause becomes essential in managing the symptoms. This may involve a combination of medications, lifestyle modifications, and therapies tailored to the specific condition. For example, addressing iron deficiency anemia through iron supplementation or incorporating regular exercise into the daily routine for managing peripheral neuropathy can help alleviate RLS symptoms.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. They can help identify any underlying medical conditions contributing to RLS and guide individuals towards the most effective management strategies.
Conclusion
In summary, while RLS is primarily a neurological disorder, it can sometimes be a symptom of an underlying medical condition. Iron deficiency anemia, peripheral neuropathy, kidney disease, diabetes, pregnancy, and Parkinson’s disease are among the conditions associated with RLS. By addressing the underlying cause, individuals can effectively manage their RLS symptoms and improve their overall quality of life. If you experience symptoms of RLS, it is crucial to seek medical attention for a proper evaluation and personalized treatment plan.
Key Takeaways: Can RLS be a symptom of another underlying medical condition?
- Restless Leg Syndrome (RLS) can sometimes be a symptom of another medical condition.
- Conditions like iron deficiency, kidney disease, and nerve damage can cause RLS.
- RLS can also be linked to pregnancy, diabetes, and certain medications.
- If you have RLS, it’s important to talk to a doctor to identify any underlying conditions.
- Treating the underlying condition can often help alleviate RLS symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
What medical conditions can cause Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS)?
While the exact cause of Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) is still unknown, it can sometimes be a symptom of an underlying medical condition. Some medical conditions that have been associated with RLS include:
1. Iron deficiency anemia: Low levels of iron in the body can lead to RLS symptoms. Iron is essential for the production of dopamine, a neurotransmitter that helps regulate muscle movement.
2. Peripheral neuropathy: Damage or dysfunction of the peripheral nerves, often caused by conditions like diabetes or chronic kidney disease, can result in RLS symptoms.
3. Chronic kidney disease: Kidney dysfunction can lead to imbalances in electrolytes and minerals, such as iron and magnesium, which can trigger RLS.
4. Parkinson’s disease: RLS is more common in individuals with Parkinson’s disease. The exact relationship between the two conditions is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to alterations in dopamine levels.
5. Pregnancy: RLS is also more prevalent during pregnancy, particularly in the third trimester. Hormonal changes and increased blood volume during pregnancy may contribute to the development of RLS symptoms.
How is Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) connected to iron deficiency?
Iron deficiency has been closely linked to Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS). Low levels of iron in the body can disrupt dopamine production, leading to RLS symptoms. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in regulating muscle movement.
Iron is necessary for the synthesis of dopamine, and when iron levels are low, dopamine production may be compromised. This can result in abnormal sensations and an irresistible urge to move the legs, characteristic of RLS. Replenishing iron stores through dietary changes or iron supplementation may help alleviate RLS symptoms in individuals with iron deficiency.
Can medications contribute to Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS)?
Yes, certain medications can contribute to the development or exacerbation of Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) symptoms. Some medications that have been associated with RLS include:
1. Antidepressants: Certain antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and tricyclic antidepressants, have been reported to trigger or worsen RLS symptoms in some individuals.
2. Antipsychotics: Some antipsychotic medications, including haloperidol and risperidone, have been linked to RLS symptoms.
3. Anti-nausea medications: Medications used to treat nausea, such as metoclopramide or prochlorperazine, have been associated with RLS symptoms in certain cases.
4. Antihistamines: Certain antihistamines, particularly older generation ones like diphenhydramine, can cause or worsen RLS symptoms.
If you suspect that your medication may be contributing to your RLS symptoms, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider. They may be able to adjust your medication regimen or recommend alternative options that are less likely to trigger RLS.
Are there any lifestyle factors that can worsen Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS)?
Yes, there are certain lifestyle factors that can worsen Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) symptoms. These include:
1. Lack of physical activity: Leading a sedentary lifestyle or spending extended periods of time in a stationary position can exacerbate RLS symptoms. Regular exercise and movement throughout the day can help alleviate symptoms.
2. Stress and anxiety: High levels of stress and anxiety can trigger or intensify RLS symptoms. Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation or deep breathing exercises, may help manage symptoms.
3. Caffeine and alcohol consumption: Both caffeine and alcohol have been known to worsen RLS symptoms in some individuals. Limiting or avoiding these substances, particularly in the evening, may help improve symptoms.
4. Certain medications: As mentioned earlier, certain medications can contribute to RLS symptoms. It is important to discuss any potential triggers with your healthcare provider.
Can treating the underlying medical condition improve Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) symptoms?
Yes, in many cases, treating the underlying medical condition associated with Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS) can lead to an improvement in symptoms. For example, addressing iron deficiency through supplementation or dietary changes can alleviate RLS symptoms in individuals with low iron levels.
Similarly, managing conditions like peripheral neuropathy, chronic kidney disease, or Parkinson’s disease may help reduce RLS symptoms. It is essential to work closely with your healthcare provider to identify and address any underlying medical conditions contributing to RLS, as this can significantly improve your quality of life.
2-Minute Neuroscience: Restless Legs Syndrome
Final Summary: Can RLS be a Symptom of Another Underlying Medical Condition?
In conclusion, Restless Leg Syndrome (RLS) can indeed be a symptom of another underlying medical condition. While RLS can occur on its own, it is often associated with other health issues such as iron deficiency, kidney disease, peripheral neuropathy, and pregnancy. Identifying and addressing these underlying conditions is crucial for effectively managing RLS symptoms and improving overall well-being.
It’s important to remember that RLS is a complex disorder with various contributing factors. By recognizing the potential connection between RLS and other medical conditions, healthcare professionals can take a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment. This may involve conducting thorough evaluations, ordering relevant tests, and collaborating with specialists from different fields to determine the most suitable treatment plan for each individual.
By understanding the link between RLS and other health conditions, individuals with RLS can advocate for themselves and work with their healthcare providers to explore potential underlying causes. This knowledge empowers them to seek appropriate medical interventions and lifestyle changes that can alleviate RLS symptoms and improve their quality of life. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to managing RLS and its associated medical conditions.